CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND
Introduction
Reading comprehension is a fundamental skill that is essential for academic success in all subjects. Students who are able to comprehend text effectively are better equipped to learn new concepts, solve problems, and engage in critical thinking.
Based on research by (Woolley, 2010) reading comprehension is a complex process that involves multiple cognitive skills, including working memory, attention, and vocabulary knowledge. (Guthrie, 2004) further emphasizes that reading comprehension is influenced by a student's prior knowledge and experiences, as well as their motivation and engagement with the text.
Additionally, a student's academic environment plays a significant role in their reading comprehension development. (Harvey 2007) highlights the importance of effective instruction and classroom practices that promote active reading strategies and provide opportunities for students to practice their comprehension skills. (Pretorius & Currin, 2010) suggests that access to a rich and diverse reading environment, including a variety of texts and resources, can also contribute to improved reading comprehension.
Researchers at Nasugbu East Senior High School are conducting a study to assess factors influencing reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement among senior high school students. The study aims to gather data on the relationship between reading comprehension skills and academic performance, providing valuable insights for the development of educational programs that can enhance student success.
Background of the Study
Reading comprehension is a crucial skill that forms the foundation for academic success across all disciplines. However, many students struggle with reading comprehension, which can lead to academic difficulties and hinder their overall educational progress. According to (Woolley, 2011), a significant number of students in senior high school exhibit challenges in reading comprehension, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of the factors that influence this skill. This study aims to investigate these factors, with the goal of identifying key areas for intervention and support to enhance student learning.
Research by Wilhelm,(2002) emphasizes the importance of a student's prior knowledge and experiences in shaping their ability to comprehend text. Students who have a strong foundation of background knowledge are better equipped to make connections between what they are reading and what they already know, leading to a deeper understanding of the material.
In lieu thereof, the researchers utilized a descriptive research design to evaluate the factors influencing reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement among senior high school students. The findings will serve as the basis for the proposed educational program for students that will contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject.
Statement of the Problem
This study aims to assess the factors influencing reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement among senior high school students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas, Academic Year 2024-2025.
Specifically, the study sought answers to the following question:
1. What role does parental involvement plays on academic achievement in senior high school students?
2. How do the level of classroom engagement during reading activity affect reading comprehension and academic performance?
3. What intervention should be implemented to enhance reading comprehension and subsequently improve academic achievement?
Scope and limitations of the study
This study focuses on assessing the factors influencing reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement among senior high school students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas, during the academic year 2024-2025. The research aims to identify and analyze the specific factors that contribute to or hinder students' reading comprehension abilities and how these factors relate to their overall academic performance.
The study's scope is limited to Senior High School Students enrolled in various academic tracks at Nasugbu East Senior High School, with a particular focus on Humanities and Social Sciences students. The data will be primarily gathered through surveys and interviews with students, teachers, and parents to gain insights into the factors influencing reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement. The findings will inform the development of targeted interventions and strategies to enhance reading comprehension skills and improve academic performance among students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, specifically within the Humanities and Social Sciences tracks.
Definition of Terms
These are the conceptual and operational definitions of the following words and phrases used in this study for clearer understanding of the research:
1.Cognitive: Cognitive is an emerging discipline that studies the cognitive properties of natural languages and the cognitive models of linguistics in cognitive computing and computational intelligence. (Wang& Berwick, 2012). In this study, it refers to the mental processes involved in understanding, reasoning, and processing information during reading comprehension.
2.Prior Knowledge: Prior knowledge refers to the existing knowledge, experiences, and skills that a developing writer brings to the task of learning to write in school, which influences their understanding of how to produce written texts and their confidence in writing. (Myhill, (2005). In this study, it refers to the information and experiences that students already have before engaging with new text, which influences their ability to comprehend the material. In this study, it refers to the information and experiences that students already have before engaging with new text, which influences their ability to comprehend the material.
3. Engagement: Engagement refer to involvement, commitment, passion, enthusiasm, absorption, focused effort, zeal, dedication, and energy. (Macey & Schneider. (2008). In this study, it refers to the students’ active participation and interest in the text, which is crucial for successful reading comprehension.
4. Instruction In this study: Instruction in this context refers to the various methods employed, such as processing instruction (PI), meaning-based output instruction (MOI), and meaning-based drills instruction (MDI), to assess their impact on learners' acquisition of Spanish direct object pronouns and their abilities in sentence-level interpretation and production tests. (Keating & Farley, (2008). It refers to the methods and practices teachers use to help students develop their reading comprehension skills.
5. Intervention: Intervention is arguing that it distorts our understanding of interventionary practices and forms of reasoning that occurred in non-sovereign international orders. (Rosenau, (1968). In this study it refers to specific programs or strategies designed to support students struggling with reading comprehension, aimed at improving their academic performance.
6. Foundation: The foundations for this functional modelling of interactive systems are introduced. The graphical constructs of SDL are related to this model. (Broy, 1991) In this study, it refers to the essential knowledge and skills that students need in order to develop strong reading comprehension abilities.
7. Descriptive Research Design: Research design is a critical topic that is central to research studies in science, social science, and many other disciplines. (Salkind, 2010) In this study, it refers to a type of research methodology used to systematically describe the factors influencing reading comprehension among students.
8. Parental Involvement: Parental Involvement is a genuine interest in the role of parents in society generally, and in the school in particular, especially of those parents whom I consider having difficulties in making their voices heard in school and in the society at large (the invisible parents). (Bouakaz, 2007) In this study, it refers to the role that parents play in supporting their children's reading development, which can impact their comprehension abilities.
9. Classroom Engagement: Despite decades of research indicating classrooms engagement, shape students learning, and development, there is a dearth of empirically grounded research focusing specifically on observed classroom engagement as a predictor of student outcomes in community colleges. (Alicea, 2016). In this study, It refers to the level of student participation and interaction during class activities that contribute to their understanding of the material.
10. Academic Achievement: Academic Achievement refers to the successful demonstration of knowledge, skills, and competencies acquired through academic endeavors, leading to personal growth and fulfilling societal needs, as emphasized by educators striving to cultivate critical thinking abilities in students for application beyond academic settings. Karbalaei, (2012). In this study, it refers to the overall performance and success of students in their academic subjects, which is influenced by their reading comprehension skills.
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURES
The Effect of Parent-Involved Reading Activities on Primary School Students' Reading Comprehension Skills, Reading Motivation, and Attitudes towards Reading.
According to (Caliskan, 2022) the study aims to investigate how reading activities involving parents impact the reading comprehension skills, reading motivation, and attitudes towards reading of fourth-grade elementary students. Utilizing a pretest-posttest quasi-experimental design with a paired control group, data were gathered from 100 fourth graders across two primary schools. Results indicated significant differences between the experimental and control groups, suggesting that parent-involved reading activities devised by the researchers positively influenced students' reading comprehension, motivation, and attitudes. This study adds to existing research on the influence of family engagement on academic performance and emotional aspects, offering recommendations for policymakers, researchers, and practitioners.
Parent involvement, socioeconomic status and reading performance
According to (Andersen, 2021) the primary objective of this study was to investigate the role of parenting behaviors in mediating the relationship between parental socioeconomic status (SES) and the reading performance of 8-year-old children. By analyzing video recordings of parent-child interactions during challenging reading tasks in Danish public schools involving 122 participants, the research revealed that parents with low SES tended to engage with their children's problem-solving efforts in unproductive ways. This form of involvement was found to account for a third of the link between parental SES and reading performance, even after considering the children's previous academic abilities. These findings have significant implications for understanding how parents, especially those with low SES, can support or hinder their children during educational tasks like homework, and for designing interventions to enhance the quality of interactions between low SES parents and their children.
Parental involvement in the academic performance of students in Ghana: Socio-economic status
According to (Kwarteng, 2022) the purpose of the study was to assess the socioeconomic status and levels of parental involvement on the academic performance of Junior High School Students in the Upper West Akim District in Ghana. The study adopted the quantitative approach and specifically used the descriptive survey design. Simple random sampling and purposive sampling techniques were used for the selection of schools and respondents for the study. The main instrument used for data collection was questionnaire. The Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) software version 22 was used for analysis of data gathered. The study concluded that, parents’ socioeconomic status specifically; education, occupation and income levels, is an important factor that determines the academic performance of students in the Upper West Akim District. The educational and income statuses have a positive relationship with the academic performance of students.
The Effect of Parent-Involved Reading Activities on Primary School Students' Reading Comprehension Skills, Reading Motivation, and Attitudes towards Reading.
According to Caliskan, (2022) the study aims to investigate how reading activities involving parents impact the reading comprehension skills, reading motivation, and attitudes towards reading of fourth-grade elementary students. Utilizing a pretest-posttest quasi-experimental design with a paired control group, data were gathered from 100 fourth graders across two primary schools. Results indicated significant differences between the experimental and control groups, suggesting that parent-involved reading activities devised by the researchers positively influenced students' reading comprehension, motivation, and attitudes. This study adds to existing research on the influence of family engagement on academic performance and emotional aspects, offering recommendations for policymakers, researchers, and practitioners.
Parent involvement, socioeconomic status and reading performance
According to Andersen, (2021) the primary objective of this study was to investigate the role of parenting behaviors in mediating the relationship between parental socioeconomic status (SES) and the reading performance of 8-year-old children. By analyzing video recordings of parent-child interactions during challenging reading tasks in Danish public schools involving 122 participants, the research revealed that parents with low SES tended to engage with their children's problem-solving efforts in unproductive ways. This form of involvement was found to account for a third of the link between parental SES and reading performance, even after considering the children's previous academic abilities. These findings have significant implications for understanding how parents, especially those with low SES, can support or hinder their children during educational tasks like homework, and for designing interventions to enhance the quality of interactions between low SES parents and their children.
Parental involvement in the academic performance of students in Ghana: Socio-economic status
According to Kwarteng, (2022) the purpose of the study was to assess the socioeconomic status and levels of parental involvement on the academic performance of Junior High School Students in the Upper West Akim District in Ghana. The study adopted the quantitative approach and specifically used the descriptive survey design. Simple random sampling and purposive sampling techniques were used for the selection of schools and respondents for the study. The main instrument used for data collection was questionnaire. The Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) software version 22 was used for analysis of data gathered. The study concluded that, parents’ socioeconomic status specifically; education, occupation and income levels, is an important factor that determines the academic performance of students in the Upper West Akim District. The educational and income statuses have a positive relationship with the academic performance of students.
Parental Involvement as Predictor for Self-regulated Learning and Academic Achievement of Students at Secondary School Level.
According to Farook, (2020) Parental involvement is essential for child's successful learning and of essential skills. They nurture self-regulated behaviors by satisfying the necessary needs of their child. In this study a causal comparative design was used to explore the causal relationship among parental involvement, self-regulated learning and academic achievement of secondary school students. The sample was consisted of 619 students of public and private secondary schools of a metropolitan city of Pakistan selected through multistage probability sampling. Self-developed instruments PII (Parental Involvement Inventory) and ASLI (Academic Self-regulated Learning Inventory) were used to collect respondents' responses. This study revealed four key parenting dimensions; autonomy support, academic assistance, structure facilitation and relatedness that have stronger considerable effect on academic achievement as well as on self-regulated learning. These parenting dimensions are found to shape students' attitude for self-regulated learning at home settings that may cause to empower their learning at school and improves their academic grades. It is also found that parents of private secondary school students are more concerned with their Childs' learning and those students are found more self-regulated and high in their academic affairs.
Psychological Factors and the Academic Performance among High School Students: Basis for Academic Self-Engagement Program
According to Mangaoil, (2018) Students, as learners, must develop not only their intelligence but also non-intellective factors in the education or learning process. The purpose of the study was to identify the different psychological factors, specifically the study habits, attitudes, and methods which in a way influence the academic performance of students, particularly in English and Mathematics subjects among Third Year High School Students in one of the private schools in Manila, the Philippines. The descriptive and documentary method of research were generated for the qualitative analysis. The findings showed that in terms of study habits and attitudes, students are prompt in completing academic assignments and free from wasteful delay and distractions. While for their study methods, it was reflected that students have academic drive which refers to the persistence and determination to succeed in academic work. Moreover, the academic self-engagement program was designed to help the students improved the following non-intellective factors which obtained the lowest mean, particularly students’ cooperation with the educational practices and requirements; inclination to use influence and playing up to the teacher to gain special consideration; and the feeling of being isolated or rejected in the academic environment manifested by hostility which affect an academic performance.
Relation between digital tool practices in the language arts classroom and reading comprehension scores
According to Salmeron, (2023). It concerns about the negative effects of digitalization on students’ reading comprehension, empirically backed by recent meta-analyses, question the efficacy of digital tools in the language arts classroom. By analyzing data from 4 and 8th grade US students from NAEP 2017, we aimed to test the generalization of the negative association between screens use and reading comprehension test scores within language arts classrooms, and to identify teachers’ practices to support comprehension, which could reduce such a negative relationship. We used data from 149,400 4th grade and 144,900 8th grade students to predict their reading comprehension scores based on their frequency of use of digital devices in the language arts class, as well as on the specific learning activities performed with such devices. Results revealed that amount of daily use of digital devices was negatively related to scores on a reading comprehension test. In addition, teachers’ uses of digital tools to support students’ reading comprehension showed positive relations for student use of digital devices for reading projects, and negative relations for activities addressing specific reading skills, such as building and practicing vocabulary. We discuss these results in light of our current understanding of the effects of digitalization on reading.
Relation between digital tool practices in the language arts classroom and reading comprehension scores
According to Salmeron, (2023) It concerns about the negative effects of digitalization on students’ reading comprehension, empirically backed by recent meta-analyses, question the efficacy of digital tools in the language arts classroom. By analyzing data from 4 and 8th grade US students from NAEP 2017, we aimed to test the generalization of the negative association between screens use and reading comprehension test scores within language arts classrooms, and to identify teachers’ practices to support comprehension, which could reduce such a negative relationship. We used data from 149,400 4th grade and 144,900 8th grade students to predict their reading comprehension scores based on their frequency of use of digital devices in the language arts class, as well as on the specific learning activities performed with such devices. Results revealed that amount of daily use of digital devices was negatively related to scores on a reading comprehension test. In addition, teachers’ uses of digital tools to support students’ reading comprehension showed positive relations for student use of digital devices for reading projects, and negative relations for activities addressing specific reading skills, such as building and practicing vocabulary. We discuss these results in light of our current understanding of the effects of digitalization on reading.
Impact of a gamified platform in the promotion of reading comprehension and attitudes towards reading in primary education
According to Sanchez, (2023) In recent years, the concept of gamification has appeared within the educational sector as a methodological innovation. There are several studies that show the motivational advantages of using this methodology in education. However, there is a dearth of studies that analyze its influence on the promotion of reading. We carried out a quasi-experimental study with 85 fourth graders to evaluate the impact of a gamified platform on both the students’ reading comprehension and their attitudes towards reading. The results obtained revealed significant differences in favor of the experimental group with respect to a more traditional approach, regarding both reading comprehension and attitudes towards reading.
Reading Comprehension Skills: The Effect of Online Flipped Classroom Learning and Student Engagement During the COVID-19 Pandemic
According to Setyosari, (2021) the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic outbreak in the Indonesians nowadays, the public education department established the policy of the online education system to all education levels. Most educators employ an online flipped learning method to support the policy. Research aimed to measure the effect of online based-flipped classroom learning between using Microsoft Team and WhatsApp and student engagement on reading comprehension skills. The research approach was a quasi-experimental model with a 2 x 3 factorial pre-test-post-test non-equivalent control group design. The sample of this investigation was early period undergraduates of the management economics study program. Data analysis employed a two-way ANOVA test. The result confirmed that the online flipped learning scheme using Microsoft Team was better than WhatsApp in improving student engagement and reading comprehension skills. We advise English lecturers to apply better online media services, pay attention to the students.
Design of a learning dashboard to enhance reading outcomes and self-directed learning behaviors in out-of-class extensive reading
According to Yang, (2024) self-directed learning (SDL) requires students to take initiative to learn and control their own learning process. Literature highlights the importance of SDL for lifelong learning. Yet, little understanding is known regarding how to support SDL at the school level, specifically for out-of-class learning context. To fill up this gap, this research developed a learning dashboard and integrated SDL process management in GOAL system. It was implemented to provide support for out-of-class online self-directed extensive reading (SDER) at a high school level. A two-group study conducted during a three-week spring vacation found the experimental group (N = 35, with SDL support) achieved significantly more reading outcomes than the control group (N = 12, without SDL support). Detailed GOAL interaction behavior analysis of the experimental group showed that viewing learning dashboard was significantly correlated with reading outcomes as well as interactions related to SDL process management. These findings highlight positive effect of SDL support in GOAL on students' out-of-class SDER outcomes as well as their SDL behaviors. The study provided implications for research related to extensive reading and SDL support for out-of-class learning.
Theoretical Framework
This study was anchored on the Schema Theory of Reading Comprehension, primarily developed by Rumelhart (1980) and further explored by Anderson and Pearson (1984), as cited by Cruz (2023). The theory posits that reading comprehension is a dynamic process where prior knowledge (schemas) plays a critical role in interpreting and understanding new information. According to Schema Theory, learners are able to better comprehend texts when they can activate relevant background knowledge, linking it to the content they are currently engaging with.
The theory suggests that reading comprehension involves not just decoding words but also integrating information with existing knowledge frameworks, making sense of the text by fitting it into what is already known. Thus, the development of reading comprehension relies on both language proficiency and the learner’s cognitive ability to draw connections between new and pre-existing knowledge.
This theoretical framework is highly relevant to the present study, which examines the factors influencing reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement among Senior High School students. These factors may include vocabulary knowledge, prior experiences, cognitive strategies, and the learning environment. Understanding how these elements affect comprehension can inform the creation of more effective instructional strategies that support students' academic success.
Moreover, the study emphasizes the importance of this theory in designing interventions aimed at enhancing reading comprehension. By identifying key factors that contribute to successful comprehension, educators can better support students' overall academic achievement.
Conceptual Framework
This conceptual framework aims to comprehensively explore the factors that influence reading comprehension and their impact on academic achievement among senior high school students. By analyzing the interplay of various variables, this study seeks to provide insights into the complex relationship between reading comprehension and academic success.
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODS AND PROCEDURES
This chapter presents the methods of research used. It also includes the research design, locale and respondents of the study, research instrument, construction and validation of instrument, ethical considerations, data gathering procedures and statistical treatment of data.
Research Design
The study used the descriptive research design to determine the Speculative Assertion of Grade 12 students of Nasugbu East Senior High School. Based on sciber (2019), descriptive research design aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. Descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables. In this study, the method was utilized by obtaining information or data of Speculative Assertion of Grade 12 students in terms of decision making, planning strategy, evidence-based analysis, problem solving, communication with the result and feedback mechanism. The aforementioned variables were included in the research as it was deemed significant to the present study.
Locale of study
This study was conducted in Nasugbu East East Senior High School located at Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. It was founded in the year 2016. The school was headed by Principal II, with fifty – one (51) teacher and four (4) non- teaching staff. It has a total population of one thousand three hundred three (1,303) enrolled students comprising grade 11 and 12. There are a total of three hundred three (303) Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences students this School Year 2024-2025. The school offers academic strands which include Accountancy. Business and Management (ABM) strand, Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) strand, Strand, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) strand, and Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood.
Respondents of the Study
The researcher used Slovin's Formula in computing the sample size population Slovin's formula is `population. Hence, the sample size recommended using this formula was one hundred seventy-nine (179) respondents with confidence level of 95 percent and Precision Level or margin of error of 5 percent. The sampling was applicable in the present study to represent the target population. After thorough study of the problem, the respondents were chosen using Simple Random Sampling (SRS) which involves selecting individuals from the population in such a way that every individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This sampling method has an equal and likely possibility of getting selected in the sample. Since the selection of item completely depends on the possibility, therefore this method is called "Method of chance Selection".
Research Instrument
The researcher reviewed various literature in speculative assertion to construct the instruments of the study. A survey questionnaire was developed from these literatures and was utilized to gather pertinent data for the present research
Part I was about the demographic profile of the respondents in terms of age, sex, and social status.
Part II set was about Speculative Assertion of the grade 12 Senior High School Students such as speculative assertions, evidence-based analysis, It was rated on a 4- point Likert scale as follows 4-Strongly Agree, 3-Agree, 2-Disagree, 1-Strongly Disagree.
Construction, and Validation of the Instrument
The research instrument was constructed under the expert guidance of the thesis adviser. For the several items we asked our adviser for the advice and kept changing the question until they were just right. Then after the revised, we sent our questions to other expert people who know a lot about education. They looked at each item to check if they really measured what we wanted to know. This helped us to make sure our questions are valid and our study would give us the right answer and good feedback. In addition, this process of construction and validation of the instruments is to ensured that the research instruments are both reliable and valid.
Ethical Considerations
Part of the ethical consideration of this study was to secure the consent of the respondents to voluntarily participate. Before the respondents participated in the study each participant was given a copy of the consents. The researcher made sure that the consent was carefully explained to each respondent. It was further emphasized to the respondents that participation in the study was voluntary and that they have option not to participate in the study. Ethical principles were considered to preserve the integrity and dignity of the respondents.
Data Gathering Procedure
The school principal of Nasugbu East Senior High School and public-school district supervisor granted permission for the researcher to conduct this study prior to the distribution of the questionnaires. The request letter (Appendix A) was forwarded to the Office of the School Principal. Following the approval, the researcher informed the respondents of the research's goal before the survey and allowed for questions to address any concerns. Then the researcher gave the survey questionnaires to the study's target respondents, giving them plenty of time to complete them. In addition, the research sought the assistance of respondents to be able to honestly assess their Speculative Assertions. The accomplished survey questionnaire was checked by the researcher for completion of the respondents before retrieval.
Statistical Treatment of Data
The following were the statistical tools used in the study.
Problem 1. What role does parental involvement play in enhancing reading comprehension skills in Senior High School students?
Problem 2. How does the level of classroom engagement during reading activities affect students reading comprehension and academic performance
Problem 3. Challenges encountered by the respondents weighted mean and deviation. These were also used to describe factors that affected students` speculative assertions.
CHAPTER 4
PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
This part presents the data gathered, analyses and interpretation to answer the problem which this study aims to achieve.
1. Parental Involvement and Reading Comprehension
Table 1 presents the English proficiency of the respondents in terms of Listening. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents’ answers regarding maintaining focused attention on speaker’s message during listening with weighted mean of 3.07 (SD=0.622), qualitatively describes as Agree. This means that they are active, attentive and concentrated in their activities. However, understanding not only words but also emotions being depicted by the speaker has the lowest weighted mean of 2.55 (SD=0.729) which means students appreciate the topics. This indicator is qualitatively described as Agree.
Overall results show that the respondents mark “agree” on their listening competencies in English with grand weighted mean of 2.84 (SD=0.657).
This result is related to the study conducted by Hsieh and Huang (2020) who revealed that multimedia input combined standard accent seems more effective for the development of listening skills. This explained that additional instructional materials should be utilized to develop their listening comprehension.
Table 1 Parental Involvement and Reading Comprehension
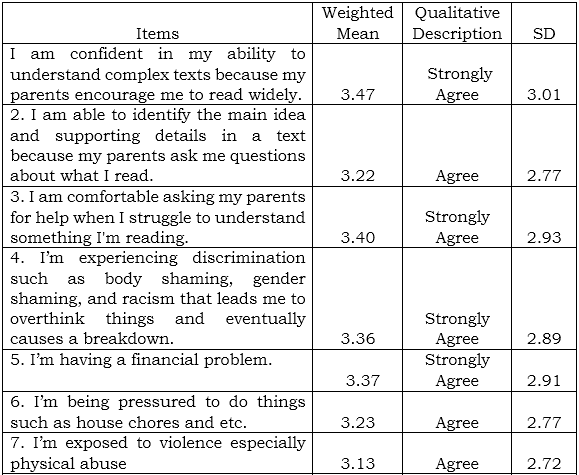
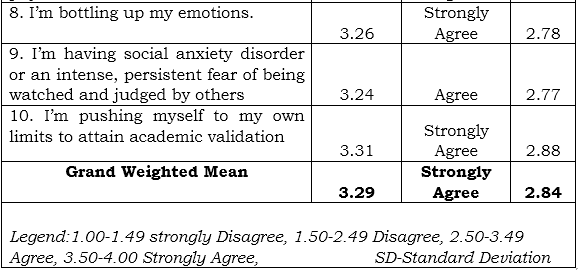
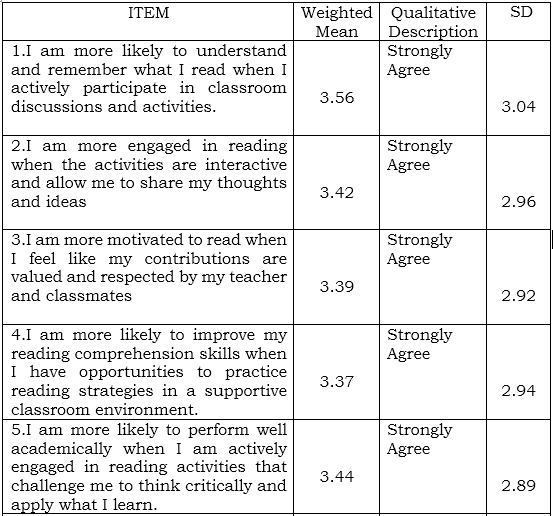
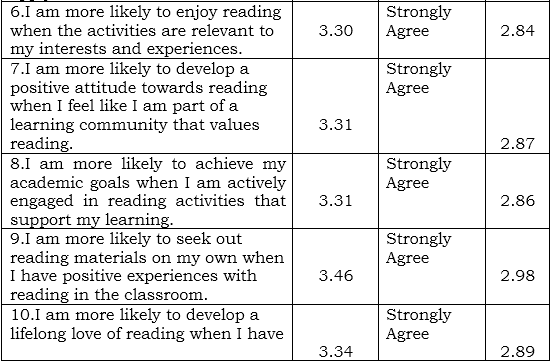
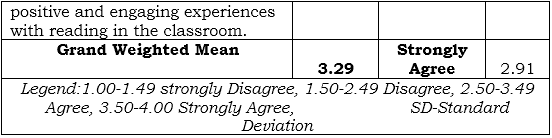
Table 2 The level of classroom engagement during reading activities affects student reading comprehension and academic performance
Table 2 presents the findings on the level of classroom engagement during reading activities and its effect on students' reading comprehension and academic performance. Two indicators were assessed. The highest weighted mean (WM) was 3.56 (SD = 2.84), reflecting strong agreement with the statement, "I am more likely to understand and remember what I read when I actively participate in classroom discussions and activities." This indicates a positive correlation between active engagement in classroom activities and students' reading comprehension skills. This finding aligns with research emphasizing the importance of active learning in improving comprehension (e.g., Freeman et al., 2014).
Conversely, the lowest WM was 3.30 (SD = 2.84) for the statement, "I am more likely to enjoy reading when the activities are relevant to my interest and experience." While this also falls within the "Agree" range, the relatively high standard deviation suggests variability in students' experiences regarding the relevance of reading activities and their enjoyment. This highlights the need for differentiated instruction that caters to diverse student interests (Tomlinson, 2014).
The overall grand weighted mean (GWM) was 3.43 (strongly agree), with a standard deviation of 2.84. This indicates a generally positive perception of the relationship between classroom engagement and reading comprehension. These findings align with existing research that emphasizes the importance of active participation and relevance in enhancing students' reading skills (e.g., Guthrie & Wigfield, 2000). Further research could investigate specific classroom strategies that promote engagement and how these strategies impact diverse student populations.
CHAPTER 5
Summary, Conclusion, and Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of findings, conclusions, and recommendations of the study.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
1. Parental Involvement and Reading Comprehension
Analysis of parental involvement revealed a strong agreement among respondents regarding their English speaking capabilities, as indicated by a grand weighted mean of 3.21 (SD = 3.01)
2. Classroom Engagement and Reading Comprehension
The researcher proposed learning activity sheets to enhance the English proficiency of Grade 12 HUMSS students at Nasugbu East Senior High School.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on findings of the study, the following conclusions are drawn:
1. Students strongly agree that parental involvement and classroom engagement significantly influence their reading comprehension skills and academic performance.
2. The proposed interventions show promise in enhancing reading comprehension and improving academic achievement among senior high school students.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the proceeding findings and conclusions the following recommendations are offered by the researchers:
1. Schools should actively promote parental involvement in supporting their children's reading development.
2. Teachers should implement engaging reading activities that foster active participation and deeper understanding.
3. Schools should integrate the identified effective interventions (explicit instruction, vocabulary development, graphic organizers) into their reading performance.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Woolley, G. (2010). Developing reading comprehension: Combining visual and verbal cognitive skill. The Australian Journal of Language and Literacy, 33(2), 108-125. Guthrie. (2004).
Increasing reading comprehension and engagement through concept-oriented reading instruction. Journal of educational psycholoy, 96(3), 403.
Harvey, S.,. (2007). Strategies that work: Teaching comprehension for understanding and engagement. Stenhouse publishers. Pretorius, E. J., & Currin, S. (2010).
Do the rich get richer and the poor poorer?: The effects of an intervention programme on reading in the home and school language in a high poverty multilingual context. International Journal of Educational Development, 30(1), 67-76. Woolley, G., & Woolley, G. (2011).
Reading comprehension (pp. 15-34). Springer Netherlands. Wilhelm, J. D. (2002). Action strategies for deepening comprehension. Scholastic Inc.. Wang, Y., & Berwick, R. C. (2012).
Towards a formal framework of cognitive . Journal of Advanced Mathematics and Applications, 1(2), 250-263. Myhill, (2005).
Prior Knowledge and the (RE) Production of School Written Genres: An Analysis of British Children’s Meaning-making Resources. Writing in Context (s) Textual Practices and Learning Processes in Sociocultural Settings, 117-136. Macey, W. H., & Schneider, B. (2008).
The meaning of employee engagement. Industrial and organizational Psychology, 1(1), 3-30. Keating, G. D., & Farley, A. P. (2008).
Processing instruction, meaning-based output instruction, and meaning-based drills: Impacts on classroom L2 acquisition of Spanish object pronouns. Hispania, 639-650. Rosenau, J. N. (1968).
The concept of intervention. Journal of International Affairs, 165-176. Broy, M. (1991). Towards a formal foundation of the specification and description language SDL. Formal Aspects of Computing, 3, 21-57. Salkind, N. J. (Ed.). (2010).
Encyclopedia of research design (Vol. 1). sage. Bouakaz, L. (2007). Parental involvement in school: What promotes and what hinders parental involvement in an urban school (Doctoral dissertation, Malmö högskola, Lärarutbildningen).
Alicea, S., Suárez-Orozco, C., Singh, S., Darbes, T., & Abrica, E. J. (2016). Observing classroom engagement in community college: A systematic approach.
Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 38(4), 757-782. Karbalaei, A. (2012). Critical thinking and academic achievement. Íkala, revista de lenguaje y cultura, 17(2), 121
Çaliskan, E. F., & Ulas, A. H. (2022). The Effect of Parent-Involved Reading Activities on Primary School Students' Reading Comprehension Skills, Reading Motivation, and Attitudes towards Reading. International Electronic Journal of Elementary Education, 14(4), 509-524.
Andersen, S. C., Gregersen, M. K., Nielsen, H. S., & Thomsen, M. K. (2021). Parent involvement, socioeconomic status and reading performance. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 65(7), 1279-1294.
Kwarteng, P., Asiamah, F., Twumasi, A. O., Nkansah, J. O., Issaka, J., & Afetorgbor, S. K. (2022). Parental involvement in the academic performance of students in Ghana: socio-economic status. Open Journal of Educational Research, 114-125 .
Farooq, M. S., & Asim, I. (2020). Parental Involvement as Predictor for Self-regulated Learning and Academic Achievement of Students at Secondary School Level. Journal of Educational Sciences & Research, 7(1).
Mangaoil, A. B. (2018). Psychological Factors and the Academic Performance among High School Students: Basis for Academic Self-Engagement Program. SIPATAHOENAN, 4(2).
Setyosari, P., Kuswandi, D., & Widiati, U. (2021). Reading Comprehension Skills: The Effect of Online Flipped Classroom Learning and Student Engagement During the COVID-19 Pandemic. European Journal of Educational Research, 10(4), 1613-1624.
Salmerón, L., Vargas, C., Delgado, P., & Baron, N. (2023). Relation between digital tool practices in the language arts classroom and reading comprehension scores. Reading and Writing, 36(1), 175-194.
Abid, N., Aslam, S., Alghamdi, A. A., & Kumar, T. (2023). Relationships among students’ reading habits, study skills, and academic achievement in English at the secondary level. Frontiers in psychology, 14, 1020269.
Prados Sánchez, G., Cózar-Gutiérrez, R., del Olmo-Muñoz, J., & González-Calero, J. A. (2023). Impact of a gamified platform in the promotion of reading comprehension and attitudes towards reading in primary education. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 36(4), 669-693.
Yang, Y., Majumdar, R., Li, H., Flanagan, B., & Ogata, H. (2024). Design of a learning dashboard to enhance reading outcomes and self-directed learning behaviors in out-of-class extensive reading. Interactive Learning Environment