ABSTRACT
This study assessed the Impact of Parental Involvement on Behavioral Outcomes of Grade 11 Humanities and Social Sciences Strand, from students of Nasugbu East Senior High School. Descriptive studies were used in the study to explain its overall conclusions. The sample population for this study consists of one-hundred eighty-three (183) Grade 11 HUMSS students. The conclusion implies that Authoritative parenting fosters a encouraging and supportive environment for their child to be confident in their abilities to tackle new challenges as senior high students.
Participants revealed that HUMSS 11 Students is related to the study conducted by Ralph McNeal Jr. (2021) Parental involvement is a much-investigated area of research. Unfortunately, there are many conflicting findings. In some cases, researchers claim parental involvement positively affects the behavior of student, while others claim parental involvement negatively affects the behavior of the student. School is a privileged context to prevent specific behavior problems. Parents are encouraged to be actively involved in the educational lives of their children regardless of the age of the children. Research has sought to understand the relationship between academic success and behavior. Research suggests that the most accurate predictor of a student’s achievement in school is neither income nor social status, but the extent to which that student’s family is able to create a home environment that encouraged learning, expressed high but not unrealistic expectations for their children’s achievement and future careers, and became involved in their children’s education at school and in the community.
Moreover, the researchers recommended to emphasize the Impact of Parental involvement that significantly influences the social behavior of Grade 11 Senior High School students. Students with active parental engagement demonstrate improved communication skills, stronger interpersonal relationships, and a higher sense of responsibility. Conducting a seminar to open and consistent communication between parents and their children positively contributes to the development of self-confidence and emotional regulation in students, enabling them to navigate social situations effectively.
CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND
Introduction
Parental involvement refers to parent’s participation in their children’s education at home and school. This can take many forms, such as helping with homework, attending school events and parent-teacher conferences, participating in decision-making processes, or regularly communicating with the child’s teacher.
According to Xitao and Michael (2001), The idea that parental involvement has positive influence on students' academic achievement is so intuitively appealing that society in general, and educators in particular, have considered parental involvement an important ingredient for the remedy for many problems in education.
In addition, Frederick and Peter (2013) special attention is paid to the children of low-educated and ethnic minority parents. Parental involvement may include classroom volunteering, chaperoning school events, participating in parent-teacher conference and other communication with teachers.
Researchers at Nasugbu East Senior High School focuses aim to examine the impact of parental involvement on behavioral outcomes in Grade 11 Senior High Student. By investigating and evaluating parental involvement effects on the behavioral outcomes of senior high students, researcher can garner valuable insights and knowledge. This research aims to contribute to a better understanding of the impact of parental involvement on behavior of students.
Background of the study
Research has shown that Parental involvement in education has long been recognized as a crucial component in supporting student success. Anthony 2022 defines that parental involvement as the active participation of parents in their children’s educational activities, both at home and at school. This involvement can take various forms, such as assisting with homework, attending school events, engaging in parent-teacher conferences, and maintaining communication with teachers. The underlying assumption is that such engagement positively impacts students’ academic and behavioral outcomes.
Student behavior encompasses a wide range of actions and reactions displayed by students, influenced by various factors such as customs, attitudes, emotions, values, ethics, power, persuasion, and genetics. Physiological factors, including being hungry, tired, or sick, may also lead to disruptive classroom behavior. In this case, children may be inattentive, cranky, or otherwise difficult, which may cause problems with their teachers or classmates. Linda 2019 research one key tactics for managing student behavior is setting behavior standards for the classroom also suggests that establishing ground rules for classroom behavior can help maintain a positive environment.
With the gathered data, the researchers applied the use of descriptive research design to assess the impact of parental involvement on the behavioral outcomes of Grade 11 Senior High School students. By examining how different forms of parental engagement affect student behavior, this research seeks to provide valuable insights into enhancing parental involvement strategies and improving student behavior in the senior high school context.
Statement of the Problem
This study aimed to assess the impact of Parental involvement on Student Behavior of Grade 11 HUMSS Students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas, Academic Year of 2024-2025.
Specifically, the study sought answers to the following questions:
1. How does Parental involvement affect social behavior of Senior High School in terms of peer relationship?
2. What role does parental communication play in shaping student behavior in Senior High School?
3. What are the interventions that should be enhance parental involvement and subsequently improve Student behavior?
Scope and Limitations of the Study
The study is focused on assessing the Impact of parental involvement on student Behavior of Grade 11 Humanities and Social Sciences at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Barangay Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. The study was limited only to Humanities and Social Sciences from the aforementioned school. The information was solely gathered form the respondents’ answers in the survey questionnaire. The findings were the bases for the proposed educational program for students that will contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject.
Definition of Terms
Parental Involvement- Parent involvement as the participation of parents in every facet of children's education and development from birth to adulthood, recognizing that parents are the primary influence in children's lives.
According to Annie 2023 Parental involvement may include classroom volunteering, chaperoning school events, participating in parent teacher conferences and other communication with teachers.
Chaperoning School Events- The act of supervising and ensuring the safety, well-being, and proper behavior of students during school-organized events.
Smith & Jones, 2019, Refers to the involvement of designated individuals, such as teachers or parents, in overseeing students during specific school events, such as field trips, sports competitions, or cultural activities.
Behavioral Outcomes- The observable actions, responses, or changes in behavior resulting from participation in or exposure to a specific activity or environment.
A study by Miller 2020 the specific attitudes, actions, or conduct displayed by students after being part of chaperoned school events, measured through surveys, interviews, or direct observation.
Physiological Factors- The physical and biological characteristics that influence an individual's state of health or responses to stimuli.
Brown et al., 2021 Refers to measurable physical conditions, such as stress levels (heart rate, cortisol levels), energy levels, or fatigue, of students or chaperones during or after school events.
Disruptive Classroom Behavior- Disruptive classroom behavior yields comparable results to other meta-analytic studies investigating the effectiveness of psychotherapy for children and adolescents. This indicates that there are efficacious treatments used in public education settings to decrease disruptive classroom behaviors.
Scott A Stage, David R Quiroz School psychology review 26 (3), 333-368, 1997. He conducted a meta-analysis of 99 studies that used interventions to decrease disruptive classroom behavior in public education settings.
Positive Environment- A positive environment is a dynamic and supportive setting where individuals feel safe, valued, and empowered to thrive. It fosters growth, learning, and well-being through mutual respect, collaboration, and a shared commitment to excellence. This environment encourages open communication, creativity, and innovation, while promoting inclusivity and diversity.
According to the study by Johnson et al., 2018, an environment characterized by constructive interactions, safety, inclusiveness, and encouragement during school events, measured through surveys assessing participants’ perceptions or qualitative observations.
Parental Engagement- The active participation and involvement of parents in their children's educational and extracurricular activities, contributing to their development and academic success.
Walker & Hoover-Dempsey, 2008. parents' attendance, support, and involvement in school events, such as volunteering, monitoring, or providing feedback, measured through attendance logs, parental surveys, or interviews.
Behavior Standards- Behavior standards are a set of official guidelines meant to actions, speech, attitudes and more. (Message Magazines, 2016) Standards that you set for yourself and others. They provide a framework for your life.
According to Eleanor (2020) A Standard Behavior a teaching model rather than a mandate for behaviour. The emphasis is on teaching rather than telling, nurturing rather than sanctioning and including rather than excluding.
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
Parental Involvement effect Student Behavior
According to Ralph McNeal Jr. (2021) Parental involvement is a much-investigated area of research. Unfortunately, there are many conflicting findings. In some cases, researchers claim parental involvement positively affects the behavior of student, while others claim parental involvement negatively affects the behavior of the student. School is a privileged context to prevent specific behavior problems. Parental involvement in school activities is crucial to promote social functioning. This study aimed to access the personnel perception of parental involvement and students’ behavior problems.
Based on the study by Peters and Thaddues J (2012). Parents are encouraged to be actively involved in the educational lives of their children regardless of the age of the children. Research has sought to understand the relationship between academic success and behavior. Research suggests that the most accurate predictor of a student’s achievement in school is neither income nor social status, but the extent to which that student’s family is able to create a home environment that encouraged learning, expressed high but not unrealistic expectations for their children’s achievement and future careers, and became involved in their children’s education at school and in the community. A strong bridge has thus linked parental involvement and academic success. In fact, many research studies suggest a direct link between parental involvement and student achievement, which is to be expected given the amount of time children spend outside of schools, presumably under the care and supervision of their parents. Therefore, students whose parents are involved in their education tend to do better in school, exhibit positive and low-risk behaviors, and associate with peers who hold similarly high standards for performance. However, what has not been clearly understood are the different ways in which a parent can be actively involved in their individual student’s success. In theory, success hinges on two-way communication between parents and teachers whereby they share common expectations and responsibility for the child’s learning. Students with involved parents, irrespective of income or background, are more likely to succeed in school and have fewer behavior problems.
A study by Ralph B McNeal Jr (2021). Parental involvement positively affects academic achievement, while others claim parental involvement negatively affects academic achievement. Finally, a third grouping of studies find parental involvement has no significant relationship to academic achievement. A parallel body of research investigating the forces affecting dropping out has also been developed. Unfortunately, little research has actually attempted to link the various dimensions of parental involvement to dropping out or other at-risk behavioral outcomes. Using the concepts of cultural and social capital, I provide a theoretical framework for why there would exist differential effects of parental involvement across cognitive and behavioral outcomes. I further investigate the variable relationships between involvement and each outcome by socioeconomic status. Findings indicate that parental involvement is generally a salient factor in explaining behavioral but not cognitive outcomes, with greatest support for parent-child discussion and involvement in Parent-Teacher organizations.
Another Study by Maria Castro (2015). Parental involvement is an individual right and responsibility for families, and a social need. It is generally accepted that without the positive cooperation of family and school, it is not possible to reach the high standards set for educational outcomes by a demanding society. In a very general sense, we could consider parental involvement as the active participation of parents in all aspects of their children's social, emotional and academic development. In a different dimension, parental involvement concerns a wide range of issues, such as parental expectations about their children's academic future, control over homework, the extent to which they become involved in helping children to learn for school assignments or to do the homework, or the frequency with which parents are physically present at school. Some of these concepts correspond to behaviors that can be promoted, or that depend on a personal parental decision. Others, such as expectations, are effects associated with third variables, which are the real causes, giving a spurious spin to the apparent correlation between parental involvement and educational achievement.
According to (Parveen et al., 2016) The main purpose of this study was to explore the impact of parental involvement on children's education. For student learning not only teachers are responsible, but their parents as well, this research aimed at exploring aspects of children's education and development in relation to parental involvement. Nancy Hill and Diana Tyson (2009) In promoting achievement among senior high school levels, the significant role of families, family - school relations and parental involvement in education has been highlighted.
Parental Communication play in shaping Student behavior
According to a study by Jurnal obsesi (2021). In shaping student behavior, it includes the family, school, and community environment. It is one of the important components that must be considered in early childhood education. One crucial element to achieve educational goals is the creation of a pleasant and comfortable environment where learning is carried out. A relaxed environment that supports the implementation of education is hugely needed and also influences the achievement of educational goals. A learning environment is place where adults become sustainable learners and give children try new things, space to explore and make learning a fun. HLE is the whole that is in the home environment and includes family interactions. Through this environment, children learn to investigate the world and know for learning in terms of attitudes and behavior through family contexts. Having a positive learning environment can foster skills and encourage active learning for early childhood.
Based on a study of S Park and S Holloway (2018). Whereas the focus of most parental involvement research has been on examining its effects on student outcomes, the goal of our study was to explore the determinants of parental involvement. Drawing on a nationally representative dataset of families with a student in high school, we investigated a hypothesized model in which positive associations between school factors (i.e., welcoming environment, informative communication, parental satisfaction with school) and levels of parental involvement in their adolescents' education are mediated by parents' construction of their role. We found that parents reportedly became involved in their children's education in response to inclusive school practices and also to compensate for perceived deficits in student experiences at school. Economically disadvantaged parents who were dissatisfied with the school were particularly likely to become involved. We also found support for a direct relationship between school factors and parental involvement, as well as an indirect path via parents' perceptions of their role in promoting their involvement.
A study by M Hammer, K Scheiter and K Stürmer (2021). Increasingly more research is exploring how digital media can be used for teaching but is largely focused on how teachers shape technology use. Besides teachers in the classroom, parents at home may also have a pivotal role in shaping students' beliefs towards digital media which are in turn an important precursor to students' use of technology for learning. Previous research shows parent factors are related to students' ICT self-efficacy; however, the underlying mechanisms explaining these relations are less clear. Following Eccles et al.’s parent socialization model (1983), we investigate whether parents' behaviors including modeling and provision of digital media mediate the relation between parents' beliefs regarding digital media and students' digital media self-efficacy.
Additionally, a study by J Bempechat, DJ Shernoff (2015). Underachievement and school disengagement have serious consequences, both at individual and societal levels. In this chapter, we adopt a strength-based perspective to examine the multiple ways in which parents foster achievement motivation and student engagement. Our theoretical orientation is grounded in Bronfenbrenner’s (1977) ecological systems theory in which the child is situated at the center of increasingly distal and interconnected spheres of influence, from family and school to community and societal institutions. Given the increasingly diverse composition of our nation’s schools, we place a premium on understanding how varied ethnic and cultural models of learning and socialization, particularly among low-income families, differentially influence parents’ educational socialization strategies and how these come to affect children’s developing achievement-related beliefs and behaviors. We examine several theoretical models of engagement, motivation, and parental involvement and highlight some notable research efforts that seek to explain parents’ roles in fostering motivation and engagement. We then share several models of innovative programs that have experienced success in creating authentic partnerships between parents, children, schools, and communities toward the goal of stemming the tide of underachievement and disengagement.
Theoretical Framework
This study was anchored on the Input Hypothesis Maintaining productive partnerships between families and schools is more complex when youth enter middle school. A systematic and inclusive understanding of the strategies parents use, youth want and need, and teachers' desire is needed to broaden our conceptualization and deepen our understanding of parental involvement in education. The authors captured the voices of 3 primary stakeholders in education (i.e., parents, teachers, and students) to identify the goals for parental involvement in education, identify consistencies across stakeholders in the conceptualizations of parental involvement in education, and deepen our understanding of the types of involvement that matter for adolescents. The study used grounded-theory analysis of 20 focus groups, with ethnically diverse parents, youth, and teachers, along with quantitative indicators of involvement and interactions with schools. From these analyses scaffolding independence, linking education to future success, and communication emerged as the most consistent strategies for promoting achievement. Conceptualizations of home-based involvement were broadened. Ethnic variations in the general experiences of families at school were highlighted.
Conceptual Framework
Based on the conceptual theory used in this study, the researcher found out that in order to make depth knowledge and careful judgement about the relationship of variables, it required critical analysis of the variables that can improve the personality development of students as well as assessing the impacts of Parental Involvement of Senior High School Students.
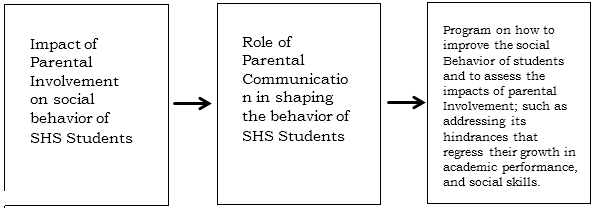 Figure (1) illustrates the study’s research simulacrum. It shows the relationship of Parental Involvement and the behavior outcomes of Grade 11 HUMSS students. Thus, the impact of the variables is determined. This study assess the impact of Parental Involvement on Behavioral outcomes of Grade 11 HUMSS students in Nasugbu East Senior High School.
Figure (1) illustrates the study’s research simulacrum. It shows the relationship of Parental Involvement and the behavior outcomes of Grade 11 HUMSS students. Thus, the impact of the variables is determined. This study assess the impact of Parental Involvement on Behavioral outcomes of Grade 11 HUMSS students in Nasugbu East Senior High School.
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODS AND PROCEDURES
This chapter presents the methods of research used. It also includes the research design, locale and respondents of the study research instrument, construction and validation of instrument, ethical considerations, data gathering procedures and statistical treatment of data.
Research Design
The study used the descriptive research design to determine the Impact of parental involvement on behavioral outcomes of Grade 11 students of Nasugbu East Senior High School. Based on Scribber 2019), descriptive research design aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon Descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables. In this study, the method was Utilized by obtaining information or data of Speculative Assertion of Grade 12 students in terms of decision making, planning strategy. evidence-based analysis, problem solving. communication with the result and feedback mechanism. The aforementioned variables were included in the research as it was deemed significant to the present study.
Locale of the Study
The study was conducted in Nasugbu East Senior High School located at Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. It was founded in the year 2016. The school was headed by Principal Il, with fifty-one (51) teachers and four (4) non-teaching staff it has a total population of one thousand three hundred three (1,384) enrolled students comprising grades 11 and 12. There are total of three hundred three (303) population of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students this School Year 2024-2025. The school offers academics which includes Accountancy, Business and Management (ABM) strand, Humanities and Social Science (HUMSS) strand, Science, Technology. Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) strand, and Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood Track (TVL).
Respondents of the Study
The researcher used Slovin's Formula in computing the sample size population. Slovin's formula is used to calculate the sample size necessary to achieve a certain confidence interval when sampling a population. Hence, the sample size recommended using this formula was one hundred seventy-nine (179) respondents with confidence level of 95 percent and Precision Level or margin of error of 5 percent. The sampling was applicable in the present study to represent the target population. After thorough study of the problem, the respondents were chosen using Simple Random Sampling (SRS) which involves selecting individuals from the population in such a way that every individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This sampling method has an equal and likely possibility of getting selected in the sample. Since the selection of items completely depends on the possibility, therefore this method is called "Method of chance Selection'".
Research Instrument
The researcher reviewed various literature in speculative assertion to construct the instruments of the study. A survey questionnaire was developed from these literatures and was utilized to gather pertinent data for the present research.
Part I Different Social pressures experienced by the HUMSS Students.
Part Il The specific sources of social pressures had the most significant impact on HUMSS Students’ Academic performance. It was rated on a 4- point Likert scale as follows 4-Strongly Agree, 3-Agree, 2-Disagree, 1-Strongly Disagree.
Construction, and Validation of the Instrument
The research instrument was Constructed under the expert guidance of the thesis adviser. For the several items we asked our expert people who know a lot about question until they were just right. Then after the revised we sent our questions to other r adviser r for the advice and kept changing the real measure of what we wanted to know. This helped us to make sure questions are out of education. They looked at each item to check if they valid and our study would give us the right answer and good feedback. In addition, this process of construction and validation of the instruments is to ensure that the research instruments is both reliable and valid.
Ethical Considerations
Part of the ethical Consideration of this study was to secure the consent of the Respondents to voluntarily participate. Before the respondents participated in this study each participant was given a copy of the consents. The researcher made sure that the consent was carefully explained to each respondent. It was further emphasized to respondents that participation in the study was voluntary and that they have the option not to participate in the study. Ethical principles were considered to preserve the integrity and dignity of the respondents.
Data Gathering Procedure
The school principal of Nasugbu East Senior High School and public-school district supervisor granted permission for the researcher to conduct this study prior to the distribution of the questionnaires. The request letter (Appendix A) was forwarded to the Office of the School Principal. Following the approval, the researcher informed the respondents of the research's goal before the survey and allowed for questions to address any concerns. Then the researcher gave the survey questionnaires to the study's target respondents, giving them plenty of time to complete them. In addition, the research sought the assistance of respondents to be able to honestly assess their Speculative Assertions. The accomplished survey questionnaire was checked by the researcher for completion of the respondents before retrieval.
Statistical Treatment of Data
The following were the statistical tools used in the study:
Problem 1. How does parental involvement effect the social behavior of senior high school students in terms of peer relationship? Frequency and percentage. These were used to indicate the percentage of observation For each profile's variable (age , sex, and socio-economic status) and also to express the relative frequency of survey responses and data.
Problem 2. What role does parental communication play in shaping the behavior of senior high school students?
Problem 3. Challenges Encountered by the Respondents: To interpret the challenges experienced by the respondents by a survey questionnaire.
CHAPTER 4
PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
This part presents the data gathered, analysis and interpretation to answer the problem which this study aims to achieve.
1. Impact of Parental Involvement on social behavior of SHS Students
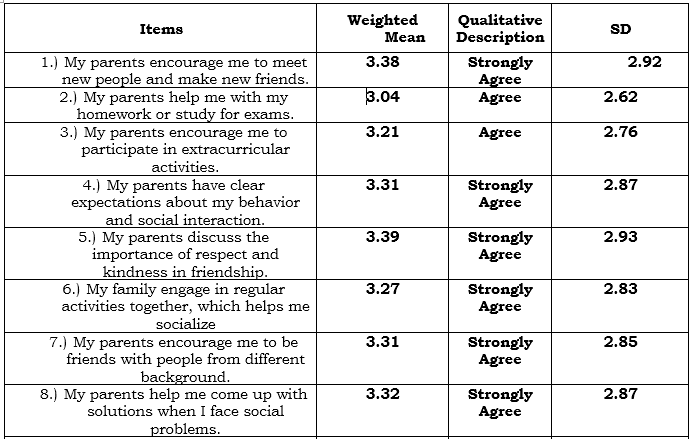
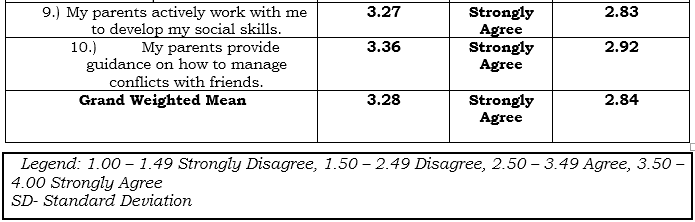
Table 1 presents the impact of Parental Involvement on social behavior. Based on the eight (8) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents’ answers that their parents discuss the importance of respect and kindness in friendship.; with weighted mean of 3.39 (SD=2.93), qualitatively describes as Agree. This means that they parents help them with my homework or study for exams. However, motivation to achieve goals because of high but achievable expectations from the parents has the lowest weighted mean of 3.02 (SD=2.62) which means students appreciate the topics. This indicator is qualitatively described as Agree.
Overall results show that the respondents mark “agree” on their Parents involvement on social behavior with grand weighted mean of 3.28 (SD=2.84).
This result is related to the study conducted by Ralph McNeal Jr. (2021) Parental involvement is a much-investigated area of research. Unfortunately, there are many conflicting findings. In some cases, researchers claim parental involvement positively affects the behavior of student, while others claim parental involvement negatively affects the behavior of the student. School is a privileged context to prevent specific behavior problems.
Table 1 Impact of Parental Involvement on social behavior of SHS Students
2. Role of Parental Communication in shaping the behavior of SHS Students
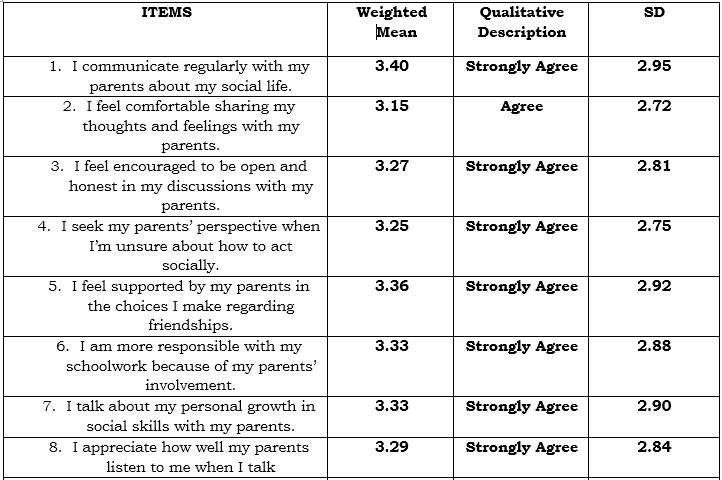
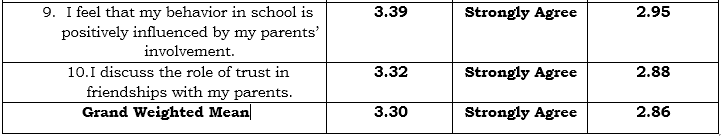
Table 2 presents the role of parental communication in shaping the behavior of SHS Students. Based on the nine (9) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents’ answers regarding the children’s communication regularly with their parents about their social life; with weighted mean of 3.40 (SD=2.95), qualitatively describes as Agree. This means that they are feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and feelings with their parents. However, good expression of feelings that are learned by parents’ open communication has the lowest weighted mean of 3.15 (SD=2.72) which means students appreciate the topics. This indicator is qualitatively described as Agree.
Overall results show that the respondents mark “agree” on their Parental Communication in shaping behavior with grand weighted mean of 3.30 (SD=2.86).
This result is related to the study conducted by Peters and Thaddues J (2012). Parents are encouraged to be actively involved in the educational lives of their children regardless of the age of the children. Research has sought to understand the relationship between academic success and behavior. Research suggests that the most accurate predictor of a student’s achievement in school is neither income nor social status, but the extent to which that student’s family is able to create a home environment that encouraged learning, expressed high but not unrealistic expectations for their children’s achievement and future careers, and became involved in their children’s education at school and in the community.
Table 2 Different Parenting Styles on Social Skills of HUMSS Students
CHAPTER 5
SUMMARY, CONCLUSION, AND RECOMMENDATION
This Chapter presents the summary of findings, conclusion, and recommendations of the study.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
1.) HUMSS 11 Senior High School Students on Impact of Parental Involvement on social behavior.
The Findings showed that respondents agreed on their Parents involvement on social behavior with grand weighted mean of 3.28 (SD=2.84).
2.) Role of Parental Communication in shaping the behavior of SHS Students.
The findings showed that the respondents agreed on their Parental Communication in shaping behavior with grand weighted mean of 3.30 (SD=2.86).
3.) This study explores how such involvement enhances children’s academic success, personal development, and overall growth. By engaging in school-related activities and supporting learning at home, parents create a positive and collaborative environment that fosters their children’s progress and achievement.
The chapter underscores that consistent Parental Involvement is a key factor in shaping well-rounded, successful individuals.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on findings of the study, the following Conclusions are drawn:
1. Respondents agree with the Impact of Parental involvement that significantly influences the social behavior of Grade 11 Senior High School students. Students with active parental engagement demonstrate improved communication skills, stronger interpersonal relationships, and a higher sense of responsibility.
2. Conducting a seminar to open and consistent communication between parents and their children positively contributes to the development of self-confidence and emotional regulation in students, enabling them to navigate social situations effectively.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the proceeding findings and conclusions the following recommendations are offered by the researcher.
1. Improved academic performance: Parental involvement is linked to better grades, higher attendance rates, and increased academic achievement in Humanities and Social Sciences.
2. Enhanced motivation : Parents' interest and encouragement foster students' motivation, self-esteem, and confidence.
3. Better time management: Parents' guidance helps students prioritize tasks, manage time effectively, and balance academic responsibilities.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Fan, X., Chen, M. Parental Involvement and Students' Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analysis.
Educational Psychology Review 13, 1–22 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009048817385
Mark Anthony. The ISME Journal, Volume 16, Issue 5, May 2022, Pages 1327–1336, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01159-7
Linda Parental involvement 2019, 11(10), 210; https://doi.org/10.3390/fi11100210
McNeal Jr, R. B. (2001). Differential effects of parental involvement on cognitive and behavioral
outcomes by socioeconomic status. The Journal of Socio-Economics, 30(2), 171-179.
Peters, T. J. (2012). Parental involvement: How does it relate to student behavior and academic success? (Doctoral dissertation, Capella University).
Castro, M., Expósito-Casas, E., López-Martín, E., Lizasoain, L., Navarro-Asencio, E., & Gaviria, J. L. (2015).
Parental involvement on student academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Educational research review, 14, 33-46. Parveen, F., Jaafar, N. I., & Ainin, S. (2016). Social media’s impact on organizational performance and entrepreneurial orientation in organizations. Management Decision, 54(9), 2208-2234.