ABSTRACT
This study examined the Assessing the Impact of Cybersecurity Education on the Behavior of Grade 11-HUMSS and selected TVL students. The study relied on descriptive studies to explain its general conclusions. The sample population for this study is one hundred ninety-four (194) respondents. Most respondents will probably Grade 11 (HUMSS) and selected (TVL) students. The conclusion implies that the senior high school students strongly agree that they have enough skills in using Cyber Security Education in terms of enhancing their understanding of digital threats and risks and being digitally aware to explore the impact of Cyber Security Education.
Besides, the respondents strongly agreed and showed that the challenges faced of the senior high school students in improving their skills in using cyber security is being aware that the cyber security is not relevant to their career goals, preventing their ability to develop and improve their knowledge in using Cyber security.
Furthermore, the researchers recommended that teachers should develop the Cybersecurity Education to enhance the understanding of Cyber Security on Senior High students that they can use for their future career.
Chapter 1
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND
Introduction
With the recent advancements of modern technology and electronics, cyber threats are also continuously evolving. Cyber Security Education is one of the ways to help defend against such threats. Grade 11 (HUMSS) and selected Grade 11 (TVL) students need to learn how to effectively protect themselves against the rise of cyber security threats.
According to Rahman et. al. (2020), despite the fact that the Internet has positively impacted people’s lives, there are negative issues emerged related to the use of Internet. Cases like cyber-bully, online fraud, racial abuse, pornography and gambling had increased tremendously due to the lack of awareness and self-mechanism among Internet users to protect themselves from being victims to these acts. Young children specifically, need to be educated to operate in a safe manner in cyberspace and to protect themselves in the process.
Furthermore, Razvan et. al. (2016), effective cybersecurity education and training are important for preparing current and future IT professionals to properly and swiftly deal with real-life security incidents.
Researchers at Nasugbu East Senior High School wants to assess the impact of Cyber Security Education on the behaviors of GRADE 11 HUMSS and selected TVL students. They also aim to gather data for the purpose of developing educational program that will provide significant insights on this topic.
Background of the Study
Research has shown that cybersecurity education is now essential in many academic fields in these days. Assessing the Impact of Cybersecurity Education on the behavior of GRADE 11 HUMSS and TVL students, which are focused nowadays and centered around the world that students need to have knowledge about cybersecurity education. As cybersecurity advances, the cyberthreats also continuous to grow such as: Phishing, Malware, Scams, data breaches are becoming more complex. In addition, cyber security platform is growing for students to learn. According to Abhishek et al. 2020, the cyber security education market has grownup exponentially, with a CAGR of 13.9 % as reported by Data Intelo. The report published by the World Economic Forum 2023 indicates a shortfall of 2.27 million cyber security experts in 2021 across different roles and hence manifest that Skill-based cyber security education is the need of the hour. Cybersecurity as a field has evolved as a multi-discipline, multi-stakeholder and multi-role discipline. Therefore, the need to address formal education with an outcome-based philosophy is imperative to address for a wider audience with varied past training in their formal education. With the Internet becoming an essential part of human life, providing security of data passed over the Internet is becoming increasingly crucial. Therefore, the role in the organization which is quite demanding is to have expertise in handling and configuring network security, a subdomain of cyber security as a priority area.
However, there are still disadvantages in cybersecurity that causes a lot of complex and lack of skilled professionals which makes cyber security challenging. Sprinto (2024) stated that while the benefits of cybersecurity are unparalleled, implementing it can be both costly and complex. There is also a lack of skilled professionals which makes it challenging. Additionally, human errors make it difficult to achieve a robust security posture. To counter sophisticated hacking practices that have evolved, organizations need to regularly update their hardware, software, and security strategy to be one step ahead of the attackers. The learning process is a continuous process as the threats are new and never-ending. Complex to setup, for setting up security architectures and tools, specialized personnel need to be employed as it is a complicated and time-consuming process. Slower systems, systems tend to become sluggish, as these security applications consume a lot of resources.
In lieu thereof, the researchers utilized the descriptive design to evaluate the Impact of Cybersecurity Education on the Behavior of Grade 11 Humss and selected TVL students in Nasugbu East Senior High School. The findings were the bases as the foundation for cybersecurity which will help students to grasp the subject for a deeper understanding.
Statement of the Problem
The study aimed to evaluate Assessing the Impact of Cybersecurity Education on the behavior of Grade 11 Humss and selected Technical Vocational Livelihood students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas, Academic year 2024-2025.
Specifically, the study sought answers to the following questions:
1. How does Cybersecurity Education influence ICT student’s awareness of cyber threats?
2. What factors influence the adoption of secure practices among ICT students?
3. What actionable proposal regarding Cybersecurity education should be develop to shape ICT student’s behaviors?
Scope and limitations of the Study
The study is focused on assessing the Impact of Cybersecurity Education on the behavior of Grade 11 Humss and selected Technical Vocational Livelihood students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Barangay, Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas.
The study was limited only to Grade 11 HUMSS and Technical Vocational Livelihood students from the Nasugbu, East, Senior High School. The data were solely gathered from the respondent’s answers in the survey questionnaire. The findings were the bases for the proposed educational program for students that will contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject.
Definitions of Terms
These are the conceptual and operational definitions of the following words and phrases used in this study of the following words and phrases used in this study for clearer understanding of the research:
Cybersecurity. It refers to the measures, practices, and technologies designed to protect computers, networks, programs, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage. According to Symantec's Internet Security Threat Report (2022), cybercrime has evolved into a major threat, with millions of cyberattacks targeting individuals, businesses, and even government infrastructures. Cybercrime has evolved into a major threat, with millions of cyberattacks targeting individuals, businesses, and even government infrastructures. ICT students are at the forefront of addressing these challenges due to their technological expertise and future roles as IT professionals.
Cyberthreats. It is any activity intended to destroy the security of an information system by altering its availability, integrity, or confidentiality. This encompasses a wide range of malicious acts that seek to damage data, steal data, or disrupt digital life in general. According to Raj Roy (2021), A cyber threat or cybersecurity threat is defined as a malicious act intended to steal or damage data or disrupt the digital wellbeing and stability of an enterprise. Cyber threats include a wide range of attacks ranging from data breaches, computer viruses, denial of service, and numerous other attack vectors. This article looks at the definition of cyber threats, types of cyber threats, and some common examples of threats. It also explores related concepts such as cyber threat intelligence and cyber threat hunting and shares the top five best practices for effective cyber threat hunting.
Education. It refers to knowledge that is received by someone who are studying or listening by someone teaching a person. It is by teaching others and by applying knowledge to an individual. According to Barry Chazan (2021), education” is sometimes traced to the Latin root educare, which means “to train” or “to mold”. Based on this linguistic root, some people like to argue that training or molding is what education today should be.
Robust. It refers to a thing that is strong or rich. According to Dictionary.com (2024), it stated that it is strong and effective in all or most situations and conditions.
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). It is used for measuring and calculating the rise and fall in value. According to Jason Fernando (2024), the compound annual growth rate is the rate of return that an investment would need to have every year in order to grow from its beginning balance to its ending balance, over a given time interval. The CAGR assumes that any profits were reinvested at the end of each period of the investment’s life span
Malware. It is a software designed to damage a computer system or to gain unauthorized access to a device. According to Rabia Tahir (2018), malwares are programs that are created to harm, interrupt or damage computers, networks and other resources associated with it.
Scams. It is by tricking people to gain important details from a victim. According to Ippei Kanehara (2023), fraud is intentional deception to secure unfair or unlawful gain, or to deprive a victim of a legal right. Fraud can violate civil law or criminal law, or it may cause no loss of money, property, or legal right but still be an element of another civil or criminal wrong.
Hardware. It is physical part of a computer in which we can touch or feel. According to Learnflyer (2021), a hardware is a physical component of a computer such as the machine and wiring, or tools and machinery.
Software. It is the part of a computer that we can not touch or feel it is because it’s inside of a computer because it’s a set of programs to perform a specific tasks. According to Manjeetks007 (2023) Software is a collection of instructions, data, or computer programs that are used to run machines and carry out particular activities.
Phishing. It is a form of stealing sensitive information by sending scams where attackers will deceive people into revealing their important things through online. According to Harry Bone (2023), Phishing scams try to trick you into revealing sensitive data or downloading malware, often leading to identity theft, credit card fraud, or other cybercrime.
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURES
The following chapter provides a thorough examination of relevant literature that pertains to the current study. This chapter includes the conceptual framework, theoretical framework, and research simulacrum.
Cyberthreats are everywhere but cybersecurity comes on the way to defend computers or servers from malicious attacks. According to Servifyspheresolutions (2024), Cyber security refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and digital information from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. It involves implementing measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, as well as safeguarding against cyber-attacks and unauthorized activities. Cyber security encompasses various strategies, technologies, and practices aimed at preventing, detecting, and responding to potential threats to ensure the security and privacy of digital assets and the overall safety of individuals, organizations, and society in the digital realm.
Influences of cybersecurity education on ICT students.
Cybersecurity is of course essential for ICT students; it influences ICT students to be aware of cyberthreats roaming around the internet. According to Kevin James (2023), revealed in their study that cybersecurity has also given an opportunity for educational institutions to be more effective and efficient in their operations. However, it is also a fact that the same technology that makes life easier for people can also make their lives miserable if it is misused. The internet and computers have become an essential part of our everyday life, no matter whether we are working or studying at home or at school or college or even at the workplace. It is therefore essential to keep the computers secure from hackers so that the personal information of students, staff members and teachers is not misused by unscrupulous people who might be interested in acquiring confidential information about students/staff/teachers without their knowledge so as to use it against them later on.
Moreover, Joanne Eliot (2022) stated that all of humanity is interconnected through the internet. People all around the world connect in cyberspace using digital devices. In doing so, each individual may divulge personal details. As each day passes, more personal information gets stored on the internet. However, access to these details makes people vulnerable to: Phishing and spamming, Ransomware, Malware and Identity theft. And also stated that students must know about cybersecurity threats and may need to learn not just for personal safety but also for studies.
In addition, Emerging India Analytics (2024) stated that prioritizing cybersecurity in education protects not only students but also educational institutions themselves from reputational damage caused by breaches or leaks of sensitive information. It is imperative for schools to invest in robust security systems and protocols to maintain confidentiality while harnessing the power of technology for effective teaching and learning experiences.
According to Halil Demirel (2024) it revealed that learning cybersecurity requires a multifaceted approach, with various options such as cybersecurity degree programs, online cybersecurity courses, and bootcamps covering different aspects of the field. Pursuing recognized cybersecurity certifications further validates and enhances expertise, contributing to developing a skilled workforce. Community activities encourage collaboration, promote skill development, and raise awareness to safeguard digital environments effectively.
Furthermore, Soc C Sirt (2023), stated that when it comes to cybersecurity education, you should keep in mind the following things educate your staff, protect sensitive data, and implement risk-management solutions. There are numerous examples of companies that have lost tons of money as well as personal information to cyberattacks.
Factors of adapting secure practices of cybersecurity on ICT students’ awareness
According to Inspiroz (2023), with the increasing use of technology in schools, cybersecurity education has become a critical component of student safety. Schools have a responsibility to protect their students' personal information and ensure that their online activities are safe and secure. Cybersecurity education can help students better understand the risks associated with using technology and how to protect themselves from cyber threats.
Moreover, Theo Zafirakos (2023) stated that cybersecurity awareness training is one of the most fundamental actionable steps that organizations can take to protect their data and other assets. In education, the potential is high for a single human error to lead to a serious security incident.
Educational institutions encounter challenges in safeguarding against cybercrime, emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity awareness. According to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach report, a data breach in the education sector costs an average of $3.65 million USD, which is slightly less costly than last year’s $3.86 million but still an alarming statistic. Another report from Check Point Research states that education and research is the most targeted industry, suffering more than 2,000 attacks per week, twice as much as other sectors. So, students and faculty members are also not safe from cyberattacks that can harm their reputation and privacy.
In addition, Fortra (2023), stated that cyber security awareness is the knowledge and understanding individuals have about protecting digital systems and data. It involves recognizing cyber threats, understanding associated risks, and adopting safe practices. This awareness aims to defend both individuals and organizations from cyber incidents, typically nurtured through training and ongoing education. This preparation is crucial in education since school districts are a treasure trove of personal data about staff, students, and their parents, making them a prime target for data breaches.
According to John Terra (2024) Security awareness training is important as it protects an organization from cyberattacks on the system resulting in data breaches. The primary focus is the prevention of such incidents that lead to loss of brand reputation and financial losses as well.
Furthermore, Luke Irwin (2022), stated that employees with poor password practices could jeopardize the security of their accounts or the confidentiality of sensitive files. Although there are technologies that can mitigate the risk, you are ultimately reliant on employees to use them appropriately and to avoid mistakes that undermine the security practices you have in place. And also stated that cyber security training is the most effective way of educating employees on the risks they should avoid and the steps they should take if they are unsure about what to do in certain scenarios.
Theoretical Framework This research is based on the Education theory cited by Sarah Buckley (2024), it states that endeavor to bridge the gap by critically analyzing the alignment of cybersecurity education literature with education theory. To this end, it will develop an ontology of learning theories and teaching styles, drawn from foundational education theory and modern education literature. This framework will be enabled to systematically analyze cybersecurity education literature, assessing the efficacy of educational methods and tools in preparing cybersecurity professionals.
The findings reveal an emphasis on "gamification" within cybersecurity education; a concept that, while moderately effective in educating the general public about basic cybersecurity concepts, falls short in adequately training cybersecurity professionals. This disproportionate focus on one method highlights the need for a more nuanced and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity education. The findings will also reveal a foundational misconception of education theory; cybersecurity education researchers are not well-educated in the field of education theory, and that is evident in the inaccuracies in inclusion of education theory in research.
The current study makes use of the theoretical perspective as it connects cybersecurity education literature with education theory. This is to assess the tools and for preparing cybersecurity education to students and by learning the basic cybersecurity concepts.
Moreover, acknowledging the importance of this theory would create a better understanding of what cybersecurity truly is. This would show how significant to ICT student to learn cybersecurity.
Conceptual Framework
Based on the explained conceptual theory used in this study, the researcher found out that in order to make deep understanding and critical examination of the variables that can improve cybersecurity education.
Figure (1) illustrates the research simulacrum of the study. It shows the relationship of influences and awareness of the ICT students in cybersecurity education. So, the impact of the variables is determined. Thus, the variables' effects are ascertained. The study's conclusions support the development of a cybersecurity education program to evaluate ICT students and help them develop and improve their computer literacy for academic purposes.
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODS AND PROCEDURES
This chapter presents the methods of research used. It also includes the research design, locale and respondents of the study, research instrument, construction and validation of instrument, ethical considerations, data gathering procedures and statistical treatment of data.
Research Design
This study used the descriptive research design to determine the Assessing the impact of cybersecurity education on the behavior of ICT students. According to Joe Eckel (2023) stated that descriptive research is a type of study used to overview characteristics of a population or phenomenon. It does not attempt to explain why something is happening. The purpose of a descriptive study is to simply describe such features of the population as age, gender, or ethnicity. Also descriptive research is used when any writer needs to describe the nature of their chosen subject. In the majority of cases, such works will contain the description of the population. Research will also use quantitative information such as statistics. The method used in this study involved gathering data or information of Assessing the impact of cybersecurity education on the behavior of ICT students.
Locale of the Study
The study was conducted in Nasugbu East Senior High School located at Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. It was founded in the year 2016. The school was headed by principal ll, with fifty-two (52) teachers and four (4) non-teaching staff and it has a total population of one thousand three-hundred ninety-two (1392) enrolled students comprises the grades 11 and 12. There are total of two hundred eighty-eight (288) population of Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood students this School Year 2024-2025. The school offers academic which includes Accountancy, Business and Management (ABM) strand, Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) strand, Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) strand, and Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood Track (TVL).
Respondents of the Study
The researchers used Slovin's Formula in computing the sample size population. Slovin's formula is used to calculate the sample size necessary to achieve a certain confidence interval when sampling a population. Hence, the sample size recommended using this formula was 194 respondents with confidence level of 95 percent and precision level or margin of error of 5 percent. The sampling was applicable in the present study to present the target population.
After through study of the problem, the respondents were chosen using Simple Random Sampling (SRS) which involves selecting individuals form the population in such a way that every individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This sampling method has an equal and likely possibility of getting selected in the sample. Since the selection of item completely depends on the possibility, therefore this method is called “Method of Chance Selection”.
Research instrument
The researcher reviewed various literature in assessing cybersecurity education on HUMSS and selected TVL students to construct the instruments of the study. A survey questionnaire was developed from these literatures and was utilized to gather pertinent data for the present research
Part I was about the Influences of cybersecurity education on GRADE 11 HUMSS and selected TVL students.
Part Il set was about Assessing cybersecurity education on GRADE 11 HUMSS and selected TVL students, it was rated on a 4-point Likert scale as follows 4-Strongly Agree, 3-Agree, 2-Disagree, 1-Strongly Disagree.
Construction, and Validation of the Instrument
The research instrument was constructed under the expert guidance of the thesis adviser. For the several items we asked our adviser for the advice and kept changing the question until they were just right. Then after the revised, we sent our questions to other expert people who know a lot about education. They looked at each item to check if they really measured what we wanted to know. This helped us to make sure our questions are valid, and our study would give us the right answer and good feedback. In addition, this process of construction and validation of the instruments is to ensure that the research instruments are both reliable and valid.
Ethical Considerations
Part of the ethical consideration of this study was to secure the consent of the respondents to voluntarily participate. Before the respondents participated in the study each participant was given a copy of the consents. The researcher made sure that the consent was carefully explained to each respondent. It was further emphasized to the respondents that participation in the study was voluntary and that they have option not to participate in the study. Ethical principles were considered to preserve the integrity and dignity of the respondents.
Data Gathering Procedure
The school principal of Nasugbu East Senior High School and public-school district supervisor granted permission for the researcher to conduct this study prior to the distribution of the questionnaires. The request letter (Appendix A) was forwarded to the Office of the School Principal. Following the approval, the researcher informed the respondents of the research's goal before the survey and allowed for questions to address any concerns. Then the researcher gave the survey questionnaires to the study's target respondents, giving them plenty of time to complete them.
In addition, the research sought the assistance of respondents to be able to honestly assess their cybersecurity education. The accomplished survey questionnaire was checked by the researcher for completion of the respondents before retrieval.
Statistical Treatment of Data
The following were the statistical tools used in the study:
Problem 1. Influences of cybersecurity education on ICT students.
Weighted Mean and Standard Deviation. These were used to indicate the influence of cybersecurity education and to express the relative mean of survey responses and data.
Problem 2. Factors of adapting secure practices of cybersecurity on ICT students’ awareness.
Weighted Mean and Standard Deviation. These were used to describe which factor that adapt secure practices for cybersecurity education.
Chapter 4
PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
This chapter presents the data gathered, analyses and interpretation to answer the problem which this study aims to achieve.
1. Influences of Cybersecurity Education on ICT Students of Cyber Threats
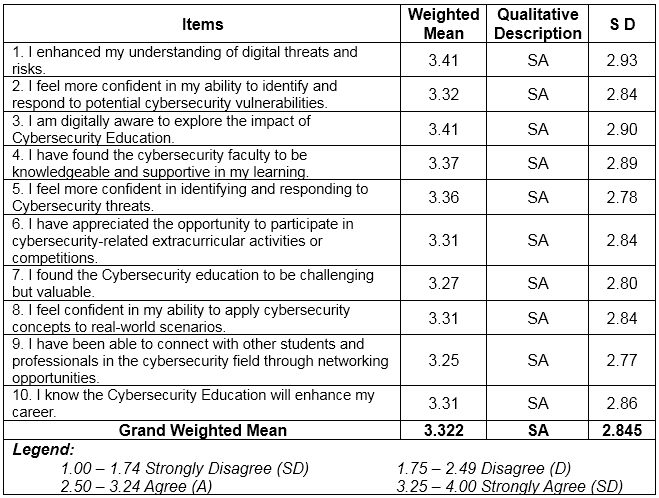
Table 1 Influence Cybersecurity Education on ICT Students of Cyber Threats. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean are the respondents' answers regarding being understood of digital threats and risks through Cyber security Education with weighted mean of 3.41 (SD= 2.93) and also digitally aware of the impact of Cyber security Education with weighted mean of 3.41 (SD=2.90), both qualitatively described as strongly agree. This means that Cybersecurity Education helps to understand and be aware of threats and risk bought by Cyberthreats, On the other hand, the lowest weighted mean is about being connected with other Students and Professionals to the Cyber Security Education helps to connect individuals
Overall results show that respondents mark “strongly agree” on their learning capabilities using ICT with grand weighted mean of 3.322 (SD=2.845).
This result is related to the study conducted by Emerging India Analytics (2024) which stated that prioritizing cybersecurity in education protects not only students but also educational institutions themselves from reputational damage caused by breaches or leaks of sensitive information. It is imperative for schools to invest in robust security systems and protocols to maintain confidentiality while harnessing the power of technology for effective teaching and learning experiences.
Table 1 Influences of Cybersecurity Education on ICT students of Cyber Threats
2. Factors Influence the adaption of cybersecurity Education among Grade 11- HUMSS and selected TVL students
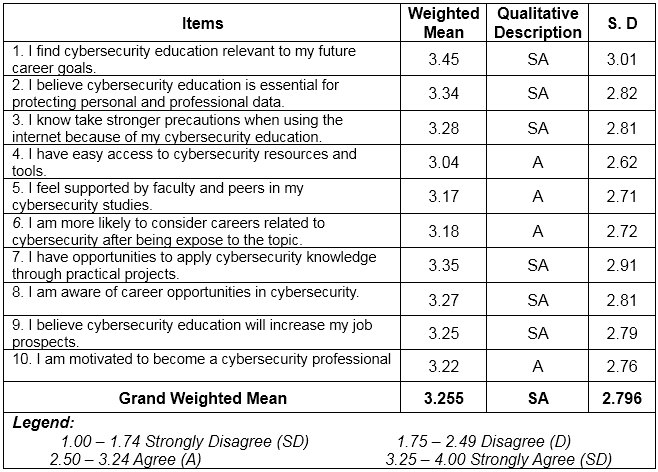
Table 2 shows The Factors Influence the Adaptation of Cyber security Education among Grade 11- HUMSS and selected TVL students. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents' answers that's Cyber security Education relevant to my future career goals with weighted mean of 3.45 (SD= 3.01), qualitatively described as strongly agree.
Overall results show that respondents mark "strongly agree” on their learning capabilities using Teaching Strategies with grand weighted mean of 3.255 (SD=2.796).
According to the study of Inspirez (2023). that with the increasing use of technology in schools, cybersecurity education has become a critical component of student safety. Schools have a responsibility to protect their students' personal information and ensure that their online activities are safe and secure. Cybersecurity education can help students better understand the risks associated with using technology and how to protect themselves from cyber threats.
Table 2 Factors of adapting secure practices of cybersecurity on ICT students’ awareness
Chapter 5
Summary, Conclusion, and Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of findings, conclusions, and recommendations of the study.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
1. Influences of Cybersecurity Education on ICT students of Cyber Threats The findings showed that respondents agree on the influence of cybersecurity education through students’ awareness with grand weighted mean of 3.322(SD=2.845).
2. Factors of adapting secure practices of cybersecurity on ICT students’ awareness
The findings showed that respondents disagree that AI lead students misuse information and ethical values with grand weighted mean of 3.255 (SD=2.796).
3. The researcher proposed cybersecurity education program to enhance the understanding of cybersecurity on Senior High School students in Nasugbu East Senior High School.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on findings of the study, the following conclusions are drawn:
1. The findings showed that respondents agreed that the cybersecurity education influence students’ awareness of cyberthreats.
2. The findings showed that respondents agreed that cybersecurity education have factors that influence the adaption of secure practices among students.
3. Cybersecurity educations are proposed to develop the students’ behavior when it comes to cybersecurity in Nasugbu East Senior High School
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the proceeding findings and conclusions the following recommendations are offered by the researchers:
1. Cybersecurity education should be developed to improve students’ awareness of cyber threats.
2. Offer cybersecurity education to all students so that they know security basics online.
Bibliography
Abhishek Vaish, Ravindra Kumar, Samo Bobek, Simona Sternad (2024). Journal of Cybersecurity Education, Research and Practice, v2024 n1 Article 22. https://eric.ed.gov/?q=Advantage+and+disadvantages+of+cyber+security+citation&id=EJ1429803
Aysuh Saxena (2024). Importance of cyber security: Benefits and Disadvantages. https://sprinto.com/blog/importance-of-cyber-security/
Barry Chazan (2021). https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-83925-3_3#Abs1
Beuran, Razvan, Chinen, Ken-ichi, Yasuo Tan, Shinoda, Yoichi (2016). Research report (School of Information Science, Graduate School of Advanced Science and Technology, Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology). https://dspace02.jaist.ac.jp/dspace/handle/10119/13769
Dictionary.com (2024). https://www.dictionary.com/browse/robust
Emerging India Analytics (2024). Cybersecurity in education: protecting student data in the digital classroom. https://medium.com/@analyticsemergingindia/cybersecurity-in-education-protecting-student-data-in-the-digital-classroom-c41291ede4a0
Halil Demirel (2024). The role of educational programs in advancing cybersecurity knowledge. https://medium.com/@halil_demirel/the-role-of-educational-programs-in-advancing-cybersecurity-knowledge-a4060be89cf3
Harry Bone (2023). https://proton.me/blog/what-is-phishing
Ippei Kanehara (2023). https://ippei.com/scam-definition/
Jason Fernando (2024). https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cagr.asp
Joanne Elliot (2022). The importance of cybersecurity for students in today’s world. https://ourcodeworld.com/articles/read/1777/the-importance-of-cybersecurity-for-students-in-todays-world
John Terra (2024). Importance of security awareness training. https://www.simplilearn.com/importance-of-security-awareness-training-article
Kevin James (2023). Importance of cybersecurity in education. https://cybersecurityforme.com/importance-of-cybersecurity-in-education/?utm_content=cmp-true
Learnflyer (2021). https://learnflyer.medium.com/what-is-hardware-what-is-software-what-are-the-differences-between-them-150b07d82dd8