ABSTRACT
This study examined the Assessing Information and Communication Technology Tools on the learning of HUMSS and TVL students: Input to proposed teachers” teaching strategies. The study relied on descriptive studies to explain its general conclusions. The sample population for this study is one hundred ninety-four (194) respondents. Most respondents will probably Grade 11 Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) students and selected Grade 11 Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood (TVL) students. The conclusion indicates that the senior high school students strongly agree that they have enough knowledge in terms of using ICT tools. They effectively manage their time for schoolworks.
Furthermore, the respondents strongly agreed and showed that the challenges faced of the senior high school students in improving their educational experience are being aware that the teacher’s are lack of strategies that can help the students to develop their knowledge for their future career, hindering their ability to develop and improve their knowledge in using ICT tools.
Besides that, the researchers recommended that teachers should develop the Information and Communication Technology tools to enhance the educational experience for the senior high school students.
CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND
Introduction
The spread of ICT tools has brought significant changes among students to interact and disseminate information and news. Smartphones are extremely important to for Senior High students because they use them for their studies and communicate even over long distances.
According to Norries et. al. (2011), smartphones do not only enable students to access and read materials, but also they can take pictures of abstract concepts that are taught in class with the camera on their smartphones so that they can relate them with concrete ideas at a later date, mostly in distance education.
In addition, the use of smartphones in learning has become the latest trend in higher education where an individual may not necessarily need a computer set to access electronic learning materials. Their phenomenal roles of the smartphone in learning have been revealed by numerous authors such as in the words of Valk et. al. (2010), that, smartphones have made learning more flexible, easy and have helped to reduce the ultimate inherent conventional classroom learning.
According to Noah Darko-Adjei (2019), smartphones made students access educational materials at anytime, anywhere and it is highly cost-effective since this opportunity is just a function of smartphones.
Researchers at Nasugbu East Senior High School want to evaluate how smartphones affect the academic performance of Senior High students. They also aim to assess the effectiveness of mobile phones in the learning process of Senior High students and to gather data on the impact of smartphones use on academic performance among students in order to create programs that will offer valuable insights on this topic.
Background of the Study
According to Tagoe and Abakah (2014) the use of smartphones can have both positive and negative effects on student’s academic performance. Smartphones enables students to engage in cooperative learning, share educational materials, and communicate in both peers and instructors. Globally, the explosion of smartphones and its related devices has greatly transformed teaching and learning in developed nations where developing nations are not the exemptions.
However too much use of smartphones can cause distraction and decrease the amount of time of students dedicate to their academic tasks. In works of woodcock et, al, (2012), it was demonstrated that students were always found using their phones for playing games and other leisure activities more that for learning. Research pointed out that although smartphones can strengthen both bridging and bonding relationships, it has only a minor effect on student’s academic achievements.
Statement of the Problem
The study aimed to evaluate the impact of ICT tools on the academic performance of Senior High students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas, Academic Year 2024-2025.
Specifically, the study sought answers to the following questions:
1. What are the specific ICT tools that have a most significant impact on the academic performance of the HUMSS and TVL students?
2. What are the specific strategies used by the teachers in the classroom setting?
3. What actionable proposals will be developed to enhance the adoption of educational experience for Senior High students.
Scope and Limitation of the Study
The study is focused on evaluating the impact of ICT tools on learning of Grade 11 HUMMS and TVL at Nasugbu East Senior High School, Barangay Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas.
The study was limited only to Senior High students from aforementioned school. The data were solely gathered from the respondents’ answers in the survey questionnaire. The findings were bases for the proposed teacher’s strategy that will contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject.
Definition of Terms
This chapter presents an intensive review of related literatures found to be relevant to the present study. This chapter likewise includes the conceptual and theoretical frameworks, and research simulacrum
Academic Achievement. Academic achievement is the amount of academic content a student learns in a specific time period. This can be any way a student has achieved short-term or long-term academic goals within an academic setting. Testing and assessments are usually performed to gauge a student’s academic achievement. ( Janelle Barowski, Vanessa Carter, 2023). In this study, it refers the achievement of the students when they acquire the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that will prepare them to lead happy and successful lives
Communication. (Adler & Proctor, 2014) When one is asked what communication is, the usual response is “talking to one another.” While this theory of communication is and can be true, the understanding of communication goes far beyond words that are merely spoken with one another. The usual models of communications such as the linear model or the transactional model, go as follows: Sender/receiver, message, the channel in which it is coming through, the noise (the distractions that disrupt transmission), the feedback and the context of the entire communication. These models alone prove that communication is merely “talking to one another
Significant. These studies suggest that “significant” can refer to statistical criteria indicating results are unlikely due to chance, practical relevance in real-world applications, or intrinsic value and broader purpose in meaningful work
Mobile Phones. Mobile devices generally refer to small and portable devices with network communication or Internet access and other functions resembling those of a computer. Such devices often include smartphones, tablets, e-book readers, some gaming devices, and handheld music tools. Mobile devices have become increasingly popular over the past few years. (Emerging Technologies for Librarians 2016). These devices have seen a significant rise in popularity due to their versatility, ease of use, and connectivity features, which align with the increasing need for on the go access to information and entertainment.
Strategy. Strategy is a plan of actions that fit together to reach a clear destination. That destination is dictated by a set of decisions that sets the organization apart from its competitors, derives from the organization’s unique characteristics, and is hard to emulate.( Tefi Alfonso, 2023). In this study, it refers to an effective detailed plan to achieve one or more long-term goals under desired conditions.
Learning. According to Filgona, Jacob and Sakiyo, John and Gwany, D. M. and Okoronka, A. U. (2020) Learning is inherently hard work; it is pushing the brain to its limits, and thus can only happen with motivation. Students’ motivation to learn is of special importance because students’ mere presence in the class is of course, not a guarantee that students want to learn. It is only a sign that students live in a society where children are required to attend school. It is important to recognize the fact that motivating learning is a central element of good teaching.
Distraction. Distraction is a process of diverting the attention of an individual or group from a desired areas of focus and thereby blocking or diminishing the reception of a desired information. Anything that takes attention away from a main goal or concentration is considered a distraction. It throws off focus, which could lower productivity or effectiveness when doing a task. Distractions can come from the outside, like noise or interruptions, or from the inside, such daydreaming or intense emotions.
Education. Education is a broad term that is related to knowledge, experience, learning, and teaching. It is a process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and habits that enable an individual to develop and grow throughout their life, for themselves or for the betterment of society. ( Kapil Verma, 2023) In this study, it refers the process to improve the quality of student learning and skills, specially in ICT to have a effective future career in technology.
Explosion. The sudden violent bursting and loud noise of something such as bomb exploding; the act of deliberately causing something to explode. In this study, It refers to the unexpected and rapid emergence or widespread proliferation of a particular phenomenon and things.
Data. Information output by a sensing device or organ that includes both useful and irrelevant or redundant information and must be processed to be meaningful. In this study, it refers to the collected information from the students.
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURES
This chapter presents an intensive review of related literatures found to be relevant to the present study. This chapter likewise includes the conceptual and theoretical frameworks, and research simulacrum.
Specific ICT tool’s that have a most significant impact on Senior High students
According to Noah Dark-Adjei (2019), the use of smartphone is gradually becoming a compelling learning tool used to enhance teaching and learning in distance education. Its usage ensures flexible course delivery, makes it possible for learners to access online learning platforms, access course resources and interact digitally.
In works of Yasan-Ak and Yildirim (2024), mobile phones have become essential learning tools with their extensive features and functionalities, contributing to the emergence of mobile learning. These devices enable communication and collaboration both inside and outside the classrooms whole also aiding in information seeking, collection, and content generation.
However, Rara et. al. (2024), stated that the development of technology today is increasingly rapid, including the use of smartphones that make it easy for users to access anything. Smartphones have a very important role for students as a tool to facilitate the learning process and do assignments.
Furthermore, Aljaber (2021), stated that the smartphone has emerged as one of the most important educational tools in today’s digital era due to its ability to facilitate access to learning materials without the traditional time and locational limitations. Smartphones and their associated applications also have the potential advantage of enhancing communication between learners and educators as well as simplifying the research process.
Moreover, Wali and Omaid stated that smartphone with its multifunctional features has gained significant importance as a must have gadget of study, work and everyday life. As an emerging trend in educational settings, many institutions are in the process of integrating smartphone into the classroom as a learning tool. Smartphone are the most powerful technological gadgets of the current time and its multi-functional features have made it a very important part of the everyday routine for almost people.
Specific strategies used by the teachers in the classroom Setting
Heidi Lutz et, al., 2024 stated that classroom management strategies are techniques that are meant to be effective in preventing problem behavior for the majority of the students in classroom setting. One such strategy, opportunity to respond, is considered as evidence-based strategy to increase engagement, improve academic achievements, and decrease behavior in the classroom.
In addition Ghavifekr & Sani, 2015 stated that ICT integration in the classroom will have a significant positive impact on teachers’ and students’ continued growth in terms of their attitudes, aptitudes, and ICT-use skills. It is reasonable to believe that the use of technological instruments and gadgets can help in learning any subject more effectively, including languages, science, math, arts, and humanities.
According to Mwila (2018), integrating ICT into the teaching and learning process improves the quality of education by making the educational process more effective and engaging for students. It is believed that ICT would make it possible to use computerization techniques in the field of education. Increasing productivity requires computerizing activity performance. Consequently, the productivity of education is greatly impacted by the use of ICT in the education sector.
Furthermore, Cheah & Lim, 2016 with the help of the World Wide Web, students can easily access online courses, interact with other students and teachers in virtual communities, and reduce their dependency on traditional classroom settings. Real learning can occur when these newly acquired skills and knowledge support and enhance what is taught in the classroom, enabling students to grasp concepts at a deeper level.
Moreover, Alonso-García et al., 2019, the move towards sustainability is an important aspect of 21st century society, and the trend to use ICT to develop good teaching practices is moving education towards these principles of sustainability. Therefore, the challenge for college teachers is to integrate all of these aspects into the classroom. All of this will lead to the sustainable use of technology, improving the quality of education through good teaching practices, while promoting environmental awareness and the creation of sustainable spaces.
According to Abik and Ajhoun (2012), integrating ICT into assimilation strategies has revealed fresh learning opportunities and trends that have served as a conduit for interaction and the dissemination of educational goal contents. However, there will not be any excellent or noteworthy results if education and objective content are not properly.
Theoretical Framework
For the purpose of this study in light of ICT integration to enhance the quality of teaching and learning experiences in school, two theories of Diffusion of Innovation by Roger’s (2023) and Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) by Davis (2003), has been identified and adopted to the research as a conceptual framework for this research (Figure 1). Roger’s theory states as a process by which an innovation is communicated through certain channels and over time among the members of a social system. The process starts with “knowledge” of the first channel that represent characteristics of the decision-making unit by the ICT users in order to integrate the technology. And it ends with “confirmation” by the users to accept the technology and integrate it accordingly. The TAM theory comprises various parts which is representing the process of ICT acceptance by the user’s including; behavioral intensions, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use. While, perceived of usefulness refers to the degree to which a person believes in the benefit from the use of a particular technology by improving job performance, perceived ease of use refers to the importance of a technology in being user-friendly for the user. Generally TAM theory was developed to measure the effectiveness or success of a technology in helping understanding the value and efficacy of a particular system. However, the theory has evolved with more specific variables explaining how a user can accept a technology over the years.
The theoretical perspective is applicable in the present study as it comprised of various aspects encompassing components in teaching strategies. Interconnectedness of this concept linked the Accessing Information and Communication Technology Tools on the learning of Senior High students: Inputs teachers teaching strategies.
Moreover, acknowledging the importance of this theory would strengthen the crafting of computer programs to enhance teaching strategies for the ICT students as it will provide substantial parameter for inputs in its realization.
Conceptual Framework
Based on the explained conceptual theory used in this study, the researcher found out that in order to make depth knowledge and careful judgment about the relationships of the variables, it required critical analysis of the variables that can enhance computer skills of the ICT students in their education.
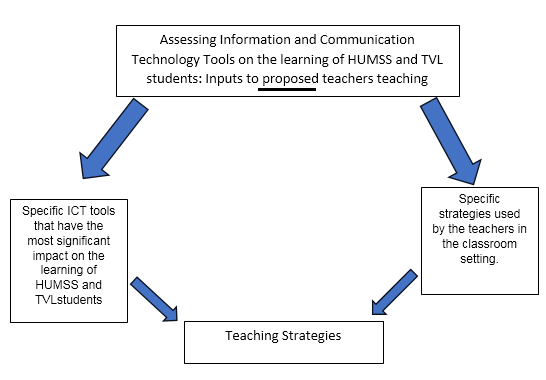
Figure 1 illustrates the research simulacrum of the study. It shows the relationship of ICT tools and teaching strategies of the teachers that affect the performance of the students. Hence, Impact of variables is determined. The findings of this study adhere to formulate learning activity sheets to develop teaching strategies leading to improve Teaching Strategies for HUMSS and TVL students in Nasugbu East Senior High School.
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND PROCEDURES
This chapter presents the methods of research used. It also includes research design, locale and respondents of the study, research instrument, construction and validation of instrument, ethical considerations, data gathering procedures and statistical treatment of data.
Research Design
The study used descriptive research design to determine the Assessing Information and Communication Technology Tools on the learning of TVL students. According to Hassan (2024), descriptive research design is a type of research methodology that aims to describe or document the characteristics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions, or perceptions of a group or population being studied. Descriptive research design does not attempt to establish cause and effect relationships between variables or make predictions about future outcomes. Instead, it focuses on providing a detailed and accurate representation of the data collected, which can be useful for generating hypotheses, exploring trends, and identifying patterns in the data. In this study, the method was utilized by obtaining information or data of Assessing Information and Communication Technology Tools on the learning of TVL students. The aforementioned variables were included in the research as it was deemed significant to the present study.
Locale of the study
The study was conducted in Nasugbu East Senior High School located at Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. It was founded in the year 2016. The school was headed by principal ll, with fifty-two (52) teachers and four (4) non-teaching staff and it has a total population of one thousand three-hundred ninety-two (1392) enrolled students comprises the grades 11 and 12. There are total of two hundred eighty-eight (288) population of Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood students this School Year 2024-2025. The school offers academic which includes Accountancy, Business and Management (ABM) strand, Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) strand, Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) strand, and Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood Track (TVL).
Respondents of the study
The researcher used Slovin’s Formula in computing the sample size population. Slovin’s formula is used to calculate the sample size necessary to achieve a certain confidence interval when sampling a population. Hence, the sample size recommended using this formula was one hundred ninety-four (194) respondents with confidence level of 95 percent and Precision Level or margin of error of 5 percent. The sampling was applicable in the present study to represent the target population.
After through study of the problem, the respondents were chosen using Simple Random Sampling (SRS) which involves selecting individuals form the population in such a way that every individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This sampling method has an equal and likely possibility of getting selected in the sample. Since the selection of item completely depends on the possibility, therefore this method is called “Method of Chance Selection”.
Research Instrument
The researcher reviewed various literature in speculative assertion to construct the instruments of the study. A survey questionnaire was developed from these literatures and was utilized to gather pertinent data for the present research.
Part I was about the specific ICT tools that have the significant impact of the academic performance of HUMSS and TVL students.
Part II was about specific teaching strategies used by the teachers in the classroom setting.
Construction and Validation of the Instruments
The research instrument was constructed under the expert guidance of the thesis adviser. For the several items we asked our adviser for advice and kept changing the questions until they were just right. Then after the revised, we sent our questions to other expert people who know a lot about education. They looked at each item to check if they really measured what we wanted to know. This helped us to make sure our questions are valid and our study would give us the right answer and good feedback. In addition, this process of construction and validation of the instruments is to ensure that the research instruments are both reliable and valid.
Ethical Considerations
Part of the ethical considerations of this study was to secure the consent of the respondents to voluntarily participate. Before the respondents participated in this study each participant was carefully explained to each respondent. It was further emphasized to the respondents that participation in the study was voluntary and that they have an option not to participate in the study.
In addition, the research sought the assistance of respondents to be able to honestly assess their ICT tools. The accomplished survey questionnaire was checked for completion of the respondents before retrieval.
Statistical Treatment of Data
The following were the statistical tools used in the study:
Problem 1. Specific ICT tools that have the most significant impact on the academic performance of HUMSS and TVL students.
Problem 2. Specific strategies used by the teachers in the classroom setting.
Chapter 4
PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
This chapter presents the data gathered, analyses and interpretation to answer the problem which this study aims to achieve.
1.ICT tools that have the most significant impact on the learning of HUMSS and TVL students
Table 1 shows the impact of ICT tools of HUMSS and TVL students in terms of Learning. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents’ answers regarding being responsible for managing personal time for effective school tasks with weighted mean of 3.42 (SD= 2.93), qualitatively described as strongly agree. This means students are responsible for managing personal time for effective school tasks. On the other hand, the lowest weighted mean is the respondents answer regarding of being better collaboration with classmate on group project with weighted mean of 3.17 (SD=2.71), qualitatively described as agree. This implies that the students are much better to collaborate with classmate on group project.
Overall results show that respondents mark “strongly agree” on their learning capabilities using ICT with grand weighted mean of 3.25 (SD=2.78).
This result is connected to a study conducted by Wali and Omaid (2020) who stated that smartphones with its multifunctional features has gained significant importance as a must have gadget of study, work and everyday life. As an emerging trend in educational settings, many institutions are in the process of integrating smartphone into the classroom as a learning tool. Smartphone are the most powerful technological gadgets of the current time, and its multi-functional features have made it a very important part of the everyday routine for almost people. This concludes that the usage of Information and Communication Technology tools should be developed to enhance the educational experience of the students.
2. The Effect of Teaching Strategies for HUMSS and TVL Students used in the Classroom Setting
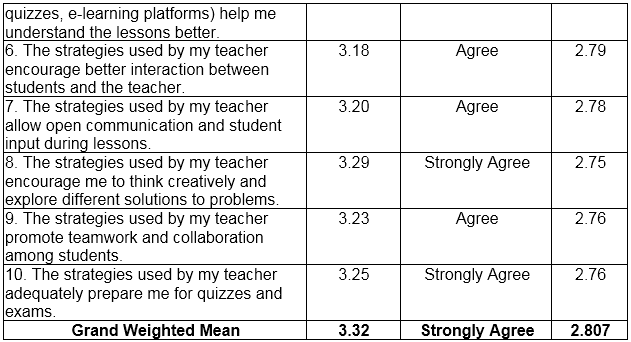
Table 2 shows the effect of teaching strategies for HUMSS and TVL Students used in the Classroom Setting. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents’ answers regarding being skilled using the strategies used by the teachers with weighted mean of 3.42 (SD= 2.94), qualitatively described as strongly agree. This means that the students are skilled in using the strategies used by the teachers. On the other hand, the lowest weighted mean is the respondents’ answers regarding being allowed to communicate with teachers and students during lessons with weighted mean of 3.20 (SD=2.78), qualitatively described as agree. This implies that the students are allowed to communicate with teachers and students during lessons.
Overall results show that respondents mark “strongly agree” on their learning capabilities using teaching strategies with grand weighted mean of 3.32 (SD=2.807).
This result is related to a study conducted by Mwila (2018), who revealed that integrating ICT into the teaching and learning process improves the quality of education by making the educational process more effective and engaging for students. It is believed that ICT would make it possible to use computerization techniques in the field of education. Increasing productivity requires computerizing activity performance. Consequently, the productivity of education is greatly impacted by the use of ICT in the education sector. Hence, information and Communication Technology tools should be established to conquer these challenges.
Table 1 ICT tools that have the most significant impact on the learning of HUMSS and TVL students.
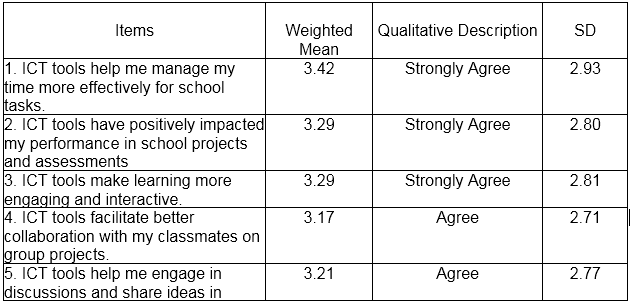
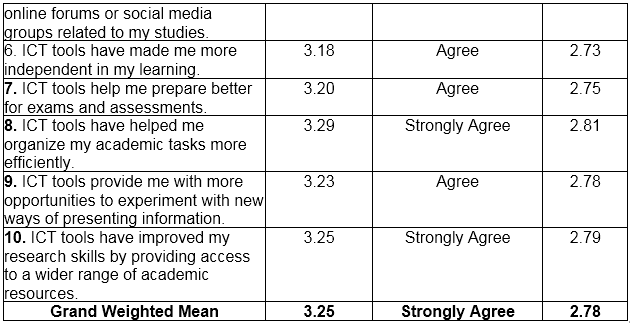
Legend: 1.00-1.74 Strongly Disagree, 1.75-2.49 Disagree, 2.50-3.24 Agree, 3.25-4.00 Strongly Agree, SD-Standard Deviation
Table 2 The Effect of Teaching Strategies for HUMSS and TVL Students used in the Classroom Setting
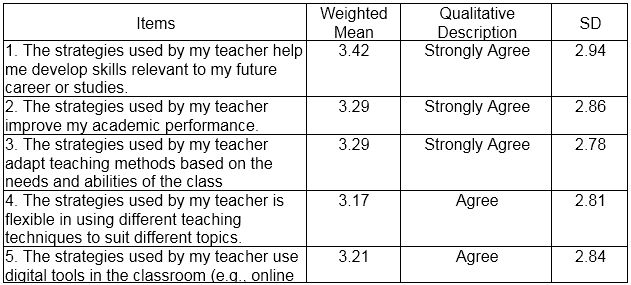
Legend: 1.00-1.74 Strongly Disagree, 1.75-2.49 Disagree, 2.50-3.24 Agree, 3.25-4.00 Strongly Agree, SD-Standard Deviation
CHAPTER 5
This chapter presents the summary of findings, conclusion, and recommendations of the study.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
1. ICT tools that have the most significant impact on the learning of HUMSS and TVL students.
The findings showed that respondents strongly agreed on their learning capabilities using ICT with grand weighted mean of 3.25 (SD=2.78).
2. The effects of teaching strategies for HUMSS and TVL Students used in the Classroom Setting.
The findings showed that respondents strongly agreed on their learning capabilities using teaching strategies with grand weighted mean of 3.32 (SD=2.807).
3. What actionable proposal will be developed to enhance the adoption of academic experience of Senior High students.
The researchers proposed that ICT tools should be developed to enhance the educational experience of students
Conclusion
Based on the findings of the study, the following conclusions are drawn:
1. The respondents agree with the ICT tools on academic performance.
2. The effect of Teaching Strategies used in the classroom setting was agreed by the respondents.
3. The development of ICT tools is proposed by the senior high students to enhance educational experience of students
Recommendation
Based on the proceeding findings and conclusions the following recommendations are offered by the researchers:
1. Teachers should develop activities that promote students’ ability to use ICT tools for managing personal tasks effectively, ensuring better learning outcomes.
2. Teachers should create projects or tasks where students can collaborate using ICT tools, improving teamwork and communication skills.
3. Teachers should implement strategies that allow students to use ICT for better communication with teachers and classmates during lessons, improving engagement in the classroom.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Abik, M., Ajhoun, R., & Ensias, L. (2012). Impact of technological advancement on pedagogy. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 13(1), 224-237.
Abdullah Awadh M. Aljaber (2021). The reality of using smartphone applications for learning in higher education of Saudi Arabia. University of Glasgow.
Cheah, H. M., & Lim, K. Y. T. (2016). Mediating approaches to the use of ICT in teaching and learning through the lenses of “craft” and “industrial”. Journal and Computers in Education, 3(1), 21-31.
Ghavifekr, S., & Mohammed Sani, I. (2015). Effectiveness of ICT integration in Malaysia Schools: Quantitative Analysis. International Research Journal for Amanti Quality in Education, 2(8), 1-12.
Heidi Lutz, Dr. Kathryn Kalafut, PhD., Dr. Tyler Re, PhD., Dr. Patty Weigand, PhD. (2024). A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of The Chicago School of Professional Psychology In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Applied Behavior Analysis.
Mwila, P. (2018). Assessing the attitudes of secondary school teachers towards the integration of ICT in teaching and learning. Process in Kilimanjaro Region, Tanzania. International Journal of Education and Development Using Information and Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 14(3), 223-258.
Noah Darko-Adjei (2019). The use and effect of smartphones in students’ learning activities: Evidence from the University of Ghana, Legon. Retrieved from
https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6260&contect+libphilprac.
Norries, C., Hossain, A., & Soloway, E. (2011). Using smartphones as essential tools for learning: A call to place schools on the right side of the 21st century. Educational Technology, 51(3), 18-25.
Rara, M., Liza, H., Asti, A., & Riri, R. (2024). Challenges and opportunities for using smartphones as learning media for students of Islamic education study program, State University of Jakarta. Journal of Social and Scientific Education, 1-8.
Tagoe, M., & Abakah, E. (2014). Determining distance education students’ readiness for mobile learning at University of Ghana using the theory of planned behavior. International Journal of Education and Development Using Information and Communication Technology, 10(1), 91.
Valk, J., Rashid, A., & Elder, L. (2010). Using mobile phones to improve educational outcomes: An analysis of evidence from Asia. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 11(1), 117-140.
Wali, A., & Omaid, M. (2020). The use of smartphones as an educational tool in the classroom: Lecturers’ perceptions. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15(16), 238-247. Kassel, Germany: International Journal of Emerging Technology in Learning.
Woodcock, B., Nortcliffe, A., & Middleton, A. (2012). Considering the smartphone learner: Developing innovation to investigate opportunities for students and their interest. Student Engagement and Experience Journal, 1(1). Yasan-Ak, N., & Yildirim, S. (2024). An investigation into smartphone use of undergraduate students in the academic environment and its predictors. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 1-33.