ABSTRACT
This study examined the AI trends on Academic Performance among Senior High School Students in Nasugbu East Senior High School: Basis for Developing AI Tools Project. The study used descriptive studies to explain its general conclusions. The sample population for this study is one hundred ninety-four (194) respondents. Respondents will probably consist of G11 Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) students and selected G11 Technical Vocational Livelihood (TVL) students. The research did how AI promotes access, collaborates, and enhances academic engagement, though a good diagnosis of some limitations, such as reduced independent learning.
Most respondents concur that AI does not trigger misuse of information as well as an inclination to infraction of ethics. Most students are able to identify both the benefits and risks of AI and use it responsibly in most situations.
The researchers recommended the development of an AI program to enhance the utilization of AI in academic performance and students must be informed about the consequences of using AI in academic performance. Schools should, therefore, introduce such programs so that competency related to AI is enhanced when the abuse is addressed. Tailor-made guidance programs are also recommended so that this valuable technological transformation could be matched with academic performance and readiness for one's career.
Chapter 1
Introduction
Al is changing many fields, including education. In ICT studies, Al tools are becoming more common, and it is important to understand how they affect student’s performance. This study will look at how using Al in ICT education impacts students' learning and achievements.
According to Paek and Kim (2021), the study "Analysis of worldwide research trends on the impact of artificial intelligence in education" examined how Al affects education, including its goals, content, methods, and evaluations. By analyzing global research trends over the past 20 years, the study identified a significant increase in the use of Al in education (AIED) research; With eight main topics of interest. It highlighted the need for more diverse and in-depth research and emphasized the benefits of applying Al technologies to education.
Similarly, Jokhan, et al., (2022), stated that Artificial intelligence (AI) is a booming technology, which has gained interest due to understanding student behavior and assessed student academic performance. AI holds great potential for improving education as it has started to develop innovative approaches to learning which effective in improving students’ academic performance.
Researchers at Nasugbu East Senior High School want to evaluate how AI trends affect academic performance of Senior High School Students in Nasugbu East Senior High School. They also aim to gather enough data to develop AI tools in improving student’s academic performance.
Background of the study
Research has shown that the usage of AI has been steadily improving over the years. With its technological advancements, it has become faster and more accurate than ever before. Sekeroglu et al. (2019) showed that Artificial Intelligence and machine learning approaches provide rapid solutions with high accuracy to assist humans. The study presented several experiments with different educational datasets to predict and classify student performances. Several machine learning models were considered for each problem and obtained results show that Artificial Intelligence can assist instructors to improve personalized education before or during the active semester.
Statement of the Problem
This study focused on evaluating rising AI trends on academic performance of ICT students in Nasugbu East Senior High School. Specifically, it aimed to find answers to the following questions.
- What are the perceptions of Senior High School students with the use of AI?
- How does AI lead students misuse information and ethical values?
- What actionable proposal should be developed next the improve the usage of AI on students academic performance?
Scope and Delimitations
This study is focused on evaluating AI trends rising trends on academic performance among Senior High School students in Nasugbu East Senior High School, Barangay Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. The study was limited only to Senior High School students within the aforementioned school. The data were solely gathered through online surveys, in which the result can be depicted in numerical form. After careful understanding of these numbers, the researchers will have a better understanding of the topic.
Definition of Terms
These are the coceptual and operational definitions if the following words and phrases used in this study for clearer understanding of the research:
Artificial Intelligence (AI). Artificial intelligence is the ability of a computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks that are commonly associated with the intellectual processes characteristic of humans, such as the ability to reason (Copeland, 2024). In this study, AI refers to the systems such as ChatGPT or other tools that automate tasks done by humans.
Machine Learning. Enables computers to imitate and adapt human-like behaviour. (Alzubi, et al., 2018). In this study, it refers to AI sytems that improves on academic through patterns based on past decisions
Perception. in humans, the process whereby sensory stimulation is translated into organized experience (William, 2024). In this study, it refers to ICT students' point of view and understanding on how AI improves academic performance and learning.
Ethical Values. are an important concept when discussing right and wrong, and this is especially so in public administration due to the myriad conflicts and dilemmas inherent in the public sector (Reed, 2018). In this study, it refers to students concern about the responsibility of using AI in terms of fairness and moral implications.
Misuse, to use something in an unsuitable way or in a way that was not intended (Cambridge Dictionary). In this study, it refers to the inappropriate or unethical use of AI tools that could negatively impact academic performance. ICT. Information and communications technology (ICT) is the use of computing and telecommunication technologies, systems, and tools to facilitate the way information is created, collected, processed, transmitted, and stored.(Rouse, 2024). In this study, it refers to the curriculum that uses tools and systems for information, and how AI affects the learning experience.
ICT Students. ICT students refer to those studying Information and Communication Technology, focusing on technologies like the internet and mobile phones for accessing and managing information in various sectors.(Singh et al., 2021). In this study, it refers to ICT students who are the main participants of this study and and how their academic performance is influence AI tools.
Academic performance. Encompasses general intellectual ability, problem-solving skills, course-related performance, approach to learning, and personal qualities, as identified in the study (Warren, 1972). In this study, it refers to students academic measurements and how AI positively or negatively affect these.
Data. Types (numbers, texts, images), sources (natural or researcher-generated) (2024). In this study data refers to the quantitative data collected from ICT students about their academic performance that will be used to improve effectiveness of AI in learning.
Trends. A trend is a new direction taken by some aspect of education that begins with a modest development and either becomes permanent or diminishes and recedes (Smith, 2016). In this study, refers to the emerging and constant change in the use of AI in the education system, specifically its application in ICT learning, and aims to assess the influence on students' academic performance.
Chapter 2
Review of Related Literature
This chapter represent an intensive review of related literatures found to be relevant to the present study.
According to Chai, et al (2021) Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly popular, and educators are paying increasing attention to it. For students, learning AI helps them better cope with emerging societal, technological, and environmental challenges. This theory of planned behaviour (TPB)-based study developed a survey questionnaire to measure behavioural intention to learn AI (n = 682) among primary school students. The questionnaire was administered online, and it measured responses to five TPB factors. The five factors were (1) self-efficacy in learning AI, (2) AI readiness, (3) perceptions of the use of AI for social good, (4) AI literacy, and (5) behavioural intention. Exploratory factor analysis and a subsequent confirmatory factor analysis were used to validate this five-factor survey. Both analyses indicated satisfactory construct validity. A structural equation model (SEM) was constructed to elucidate the factors’ influence on intention to learn AI. According to the SEM, all factors could predict intention to learn AI, whether directly or indirectly. This study provides new insights for researchers and instructors who are promoting AI education in schools.
The ethical challenges of AI in education must be identified and introduced to teachers and students. To address these issues, this paper (1) briefly defines AI through the concepts of machine learning and algorithms; (2) introduces applications of AI in educational settings and benefits of AI systems to support students’ learning processes; (3) describes ethical challenges and dilemmas of using AI in education; and (4) addresses the teaching and understanding of AI by providing recommended instructional resources from two providers—i.e., the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) Media Lab and Code.org. The article aims to help practitioners reap the benefits and navigate ethical challenges of integrating AI in K-12 classrooms, while also introducing instructional resources that teachers can use to advance K-12 students’ understanding of AI and ethics. Akgun and Greenhow (2021)
Based on Veronico Solido’s study (2023) The introduction of artificial intelligence into the field of education is driving a fundamental shift in the approaches to teaching and educational practice that are now in use. The primary purpose of this research is to evaluate the effect that artificial intelligence-driven educational resources, such as intelligent tutoring systems and virtual learning environments, have on the academic performance and comprehension of students. The findings suggest that artificial intelligence has the potential to bring about a huge revolution in the field of education by making it possible to personalise and adjust students' educational experiences in a way that boosts both students' academic performance and their overall level of comprehension.
Theoretical Framework
This study is grounded in Venkatesh et al.'s (2016) Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), as cited by Schuetz and Venkatesh (2020). UTAUT states that the adoption and usage of technology depend on some key factors, namely performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating conditions. The said factors help answer how students in Nasugbu East Senior High School view and make use of AI tools and how these will result in academic performance effects.
What would Schuetz and Venkatesh be doing by diving deeper to the cognitive computing systems, such as AI, implications for user-system interactions: challenging previous assumptions and further demonstrating how these systems change users perspectives in terms of learning and engagement. This study is important to how AI tools in education will enhance the learning processes, influencing learning students' academic outcomes.
This is inclusive of Cognitive Load Theory wherein learning is most effective when instrumental tools reduce unnecessary cognitive load. AI tools may be helpful in this by personalization of instruction, simplification of complex content, and optimal cognitive engagement of students. By reducing cognitive overload, students are likely to improve in academic performance as they would pay more attention to understanding certain aspects and being overwhelmed learning processes.
This theoretical framework will be applicable to the current study as it connects AI usage concepts to academic performance. It shall facilitate understanding how AI can make learning easier by providing personalized instruction and cognitive support, leading to better academic performance. Understanding the following theories will help in the development of AI tools for improving the academic performance of students at Nasugbu East Senior High School, specifically to help address academic performance with innovative solutions through the use of technology.
Conceptual Framework
Conceptual Framework Based on the explained conceptual theory used in this study, the researcher found out that in order to make depth knowledge and careful judgment about the relationships of the variables, it required critical analysis of the variables that can enhance Computer programming of Senior High School students.
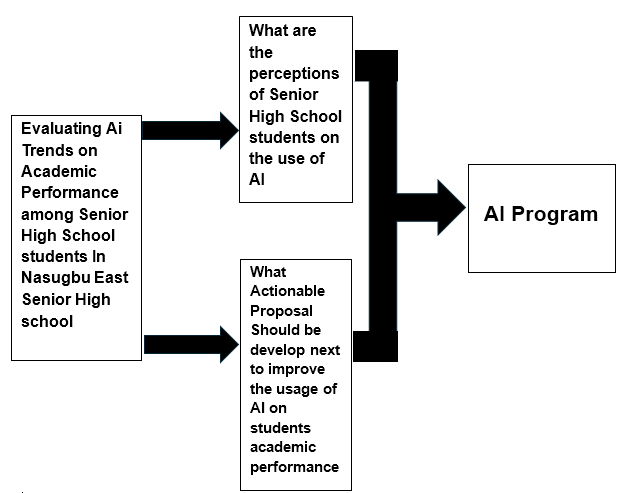
Figure (1) illustrates the research simulacrum of the study. It shows the relationship of the perceptions of Senior High School students on the use of AI and Actionable Proposal Should be develop next to improve the usage of AI that affect the performance of the students. Hence, Impact of the variables is determined. The findings of this study adhere to formulate AI program to enhance their computer programming leading to improve perceptions of Senior High School students on the use of AI of Grade 11 Humms students and selected TVL students in Nasugbu East Senior High School.
Chapter 3
RESEARCH METHODS AND PROCEDURES
This chapter presents the methods of research used. It also includes the research design, locale and respondents of the study, research instrument, construction and validation of instrument, ethical considerations, data gathering procedures and statistical treatment of data.
Research Design
The study used the descriptive research design to determine the Evaluating Ai trends on academic performance Among Senior High School students in Nasugbu East Senior High School. According to Longe (2020), Descriptive research is a type of research that describes a population, situation, or phenomenon that is being studied. It focuses on answering the how, what, when, and where questions If a research problem, rather than the why. In this study, the method was utilized by obtaining information or data of evaluating ai trends on academic performance Among Senior High School students. The aforementioned variables were included in the research as it was deemed significant to the present study.
Locale of the Study
The study was conducted in Nasugbu East Senior High School located at Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. It was founded in the year 2016. The school was headed by principal ll, with fifty-two (52) teachers and four (4) non-teaching staff and it has a total population of one thousand three-hundred ninety-two (1392) enrolled students comprises the grades 11 and 12. There are total of three hundred thirty five (335) population of Humanities and Social Sciences and total of selected Technological Vocational Livelihood students (37) this School Year 2024-2025. The school offers academic which includes Accountancy, Business and Management (ABM) strand, Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) strand, Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) strand, and Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood Track (TVL).
Respondents of the Study
The researchers used Slovin’s Formula in computing the sample size population. Slovin’s formula is used to calculate the sample size necessary to achieve a certain confidence interval when sampling a population. Hence, the sample size recommended using this formula was 194 respondents with confidence level of 95 percent and precision level or margin of error of 5 percent. The sampling was applicable in the present study to present the target population. After through study of the problem, the respondents were chosen using Simple Random Sampling (SRS) which involves selecting individuals form the population in such a way that every individual has an equal chance of being choosen. This sampling method has an equal and likely possiblity of getting selected in the sample. Since the selection of item completely depends on the possibilty, therefore this method is called “Method of Chance Selection”.
Research instrument
The researcher reviewed various literature in evaluating the use of AI on students academic performance to construct the instruments of the study. A survey questionnaire was developed from these literatures and was utilized to gather pertinent data for the present research Part I was about the perceptions of Senior High School students on the use of AI. Part Il set was about evaluating AI trends on academic performance Among Senior High School students in Nasugbu East Senior High School, It was rated on a 4-point Likert scale as follows 4-Strongly Agree, 3-Agree, 2-Disagree, 1-Strongly Disagree.
Construction, and Validation of the Instrument
The research instrument was constructed under the expert guidance of the thesis adviser. For the several items we asked our adviser for the advice and kept changing the question until they were just right. Then after the revised, we sent our questions to other expert people who know a lot about education. They looked at each item to check if they really measured what we wanted to know. This helped us to make sure our questions are valid and our study would give us the right answer and good feedback. In addition, this process of construction and validation of the instruments is to ensured that the research instruments is both reliable and valid.
Ethical Considerations
Part of the ethical consideration of this study was to secure the consent of the respondents to voluntarily participate. Before the respondents participated in the study each participant was given a copy of the consents. The researcher made sure that the consent was carefully explained to each respondent. It was further emphasized to the respondents that participation in the study was voluntary and that they have option not to participate in the study. Ethical principles were considered to preserve the integrity and dignity of the respondents.
Data Gathering Procedure
The school principal of Nasugbu East Senior High School and public-school district supervisor granted permission for the researcher to conduct this study prior to the distribution of the questionnaires. The request letter (Appendix A) was forwarded to the Office of the School Principal. Following the approval, the researcher informed the respondents of the research's goal before the survey and allowed for questions to address any concerns. Then the researcher gave the survey questionnaires to the study's target respondents, giving them plenty of time to complete them. In addition, the research sought the assistance of respondents to be able to honestly assess their Speculative Assertions. The accomplished survey questionnaire was checked by the researcher for completion of the respondents before retrieval.
Statistical Treatment of Data
The following were the statistical tools used in the study: Problem 1. Peceptions of Senior High School students on the use of AI. Weighted Mean and Standard Deviation.These were used to indicate the perceptions of Senior High School students on the use of AI and also to express the mean of survey responses and data. Problem 2. AI lead students to misuse information and ethical values. Weighted Mean and Standard Deviation. These were also used to describe factors that affected students' speculative assertions.
Chapter 4
PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
This chapter presents the data gathered, analyses and interpretation to answer the problem which this study aims to achieve.
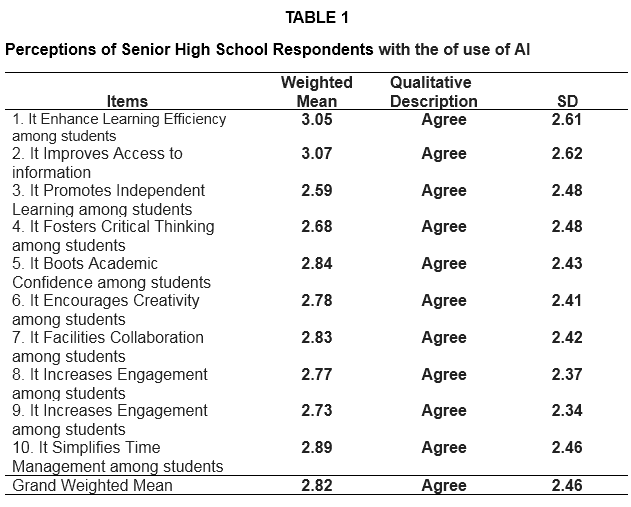
1. Perceptions of Senior High School students with the use of AI
Table 1 shows the perceptions of Senior High School respondents with the use of AI. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents' answers about improving access to information with weighted mean of 3.07 (SD= 2.62), qualitatively described as agree. This means that AI helps improve their studies however, promoting independent learning among students has the lowest weighted mean of 2.59 (SD=2.48), qualitatively describes as Agree. This implies that AI promotes learning among students by their own knowledge.
Overall results show that respondents mark” Agree” on their use of AI with grand weighted mean of 2.82 (SD=2.46). However, there are factors that affect students' skills in use of AI.
This result is related to the study conducted by Chai, et al (2021) who revealed that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly popular, and educators are paying increasing attention to it. For students, learning AI helps them better cope with emerging societal, technological, and environmental challenges. This theory of planned behaviour (TPB)-based study developed a survey questionnaire to measure behavioural intention to learn AI (n = 682) among primary school students. The questionnaire was administered online, and it measured responses to five TPB factors. The five factors were (1) self-efficacy in learning AI, (2) AI readiness, (3) perceptions of the use of AI for social good, (4) AI literacy, and (5) behavioural intention. Exploratory factor analysis and a subsequent confirmatory factor analysis were used to validate this five-factor survey. Both analyses indicated satisfactory construct validity. A structural equation model (SEM) was constructed to elucidate the factors’ influence on intention to learn AI. According to the SEM, all factors could predict intention to learn AI, whether directly or indirectly. This study provides new insights for researchers and instructors who are promoting AI education in schools. This explains that teachers utilize AI program that help students enhance their abilities in use of AI.
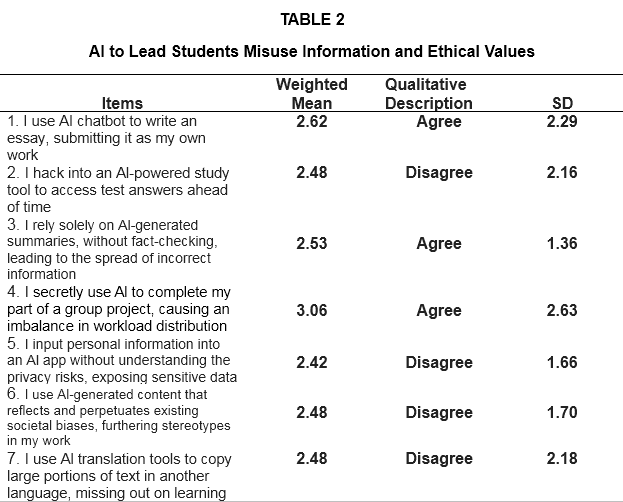
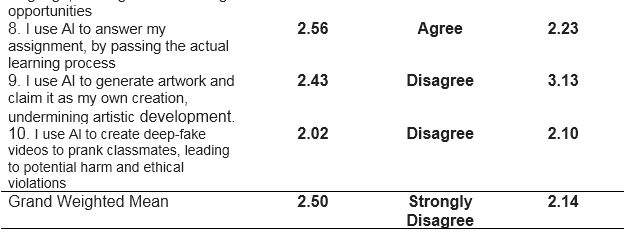
2. AI to Lead Students Misuse Information and Ethical Values
On table 2 shows how does AI lead Senior High School respondents in misuse information and ethical values. Based on the ten (10) indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest Weighted Mean is the respondents’ answers about secretly using AI to complete group works with weighted mean of 3.06 (SD= 2.63), qualitatively described as agree. This suggests that students would hide their use of AI for cheating in group work, with a weighted mean of 3.06 (SD=2.63), qualitatively described as Agree. In contrast, the use of AI to create deepfake videos to play pranks on classmates had the lowest weighted mean of 2.02, described as Disagree, which indicates general awareness of ethical concerns and possible violations from misuse.
Overall results show that respondents mark agree on their use of AI with grand weighted mean of 2.50 (SD=2.14). However, there are factors that affect students' skills in use of AI. This explains that teachers utilize AI program that help students enhance their abilities in use of AI.
This result is related to the study conducted by Akgun and Greenhow (2021) who presented that the ethical challenges of AI in education must be identified and introduced to teachers and students. To address these issues, this paper (1) briefly defines AI through the concepts of machine learning and algorithms; (2) introduces applications of AI in educational settings and benefits of AI systems to support students’ learning processes; (3) describes ethical challenges and dilemmas of using AI in education; and (4) addresses the teaching and understanding of AI by providing recommended instructional resources from two providers—i.e., the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) Media Lab and Code.org. The article aims to help practitioners reap the benefits and navigate ethical challenges of integrating AI in K-12 classrooms, while also introducing instructional resources that teachers can use to advance K-12 students’ understanding of AI and ethics.
Chapter 5
Summary, Conclusion, and Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of findings, conclusions, and recommendations of the study.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
1. Perception of Senior High School students with the use of AI
The findings showed that respondents agreed on their perception with the use of AI with grand weighted mean of 2.82 (SD=2.46).
2. AI to lead students misuse information and ethical values.
The findings showed that respondents disagree that AI lead students misuse information and ethical values with grand weighted mean of 2.50(SD=2.14).
3. The researcher proposed AI program to enhance the usage of AI of Senior High School students in Nasugbu East Senior High School.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on findings of the study, the following conclusions are drawn:
1. The findings showed that respondents agreed on their perception with the use of AI.
2. The findings showed that respondents disagree that AI lead students misuse information and ethical values.
3. AI program are proposed to improve usage of AI of Senior High School students in Nasugbu East Senior High School
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the proceeding findings and conclusions the following recommendations are offered by the researchers:
1. AI program should be developed to enhance the usage of AI in Academic performance
2. Students must be aware of the consequences of using AI in Academic performance.
REFERENCES:
1. Akgun, S., & Greenhow, C. (2022). Artificial intelligence in education: Addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings. AI and Ethics, 2(3), 431–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-021-00096-7
2. Alzubi, Jafar, Nayyar, Anand, & Kumar, Akshi (2018). “Machine Learning from Theory to Algorithms: An Overview.” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1142 012012. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1142/1/012012/meta
3. Anton, Smith. (2016). Research in Reading: Trends and Implications. https://typeset.io/papers/research-in-reading-trends-and-implications-2mhb5inhdu
4. Anjeela Jokhan, Aneesh A Chand, Vineet Singh, Kabir A Mamun (2022). “Increased digital recourse consumption in higher educational institutions and the artificial intelligence role in informing decisions related to student performance.” Sustainability, 14(4), 2377. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=evaluating+AI+trends+on+academic+performance+of+ICT+students+&btnG=#d=gs_qabs&t=1723698850410&u=%23p%3DcDmomud2rUMJ
5. Boran Sekeroglu, Kamil Dimililer, and Kubra Tuncal (2019). “Artificial Intelligence in Education: Application in student performance evaluation.” Dilemas Contemporaneos: Educacion, Politica y Valores, 7(1), 2019. https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A4%3A11148708/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A139026813&crl=c
6. Chai, C. S., Lin, P.-Y., Jong, M. S.-Y., Dai, Y., Chiu, T. K. F., & Qin, J. (2021). Perceptions of and Behavioral Intentions towards Learning Artificial Intelligence in Primary School Students. Educational Technology & Society, 24(3), 89–101. https://www.jstor.org/stable/27032858
7. Copeland, B. (2024, September 12). Artificial Intelligence. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence
8. Dember, W. N., West, L. Jolyon, & Epstein, W. (2024, August 16). Perception. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/perception
9. Jafar Alzubi, Anand Nayyar, and Akshi Kumar (2018). “Machine Learning from Theory to Algorithms: An Overview.” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1142 012012. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1142/1/012012/meta
10. Jonathan, R., Warren. (1972). Varieties of Academic Performance. https://typeset.io/papers/varieties-of-academic-performance-5evdrekv02
11. Longe, B. (2020). “Descriptive Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods.” Formplus. Descriptive Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods (formpl.us)
12. Margaret Rouse (2024). “Information and Communication Technology (ICT).” https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24152/information-and-communications-technology-ict
13. Misuse. https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/misuse
14. Paek, Seungsu, and Kim, Namhyoung. (2021). “Analysis of worldwide research trends on the impact of artificial intelligence in education.” Sustainability, 13(14), 7941. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=AI+trends+on+academic+performance&oq=#d=gs_qabs&t=1723643344659&u=%23p%3D3iT-beLvM8gJ
15. Reed, G. (2018). Ethical Values. In: Farazmand, A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20928-9_942
16. Salido, Veronica. (2023). Impact of AI-Powered Learning Tools on Student Understanding and Academic Performance. 10.13140/RG.2.2.17259.31521. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/376260972_Impact_of_AI-Powered_Learning_Tools_on_Student_Understanding_and_Academic_Performance/citations
17. Schuetz, Sebastian & Venkatesh, Viswanath. (2020). The Rise of Human Machines: How Cognitive Computing Systems Challenge Assumptions of User-System Interaction. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 21(2), 460–482. https://ssrn.com/abstract=3680306
18. Shani, Kumar, Singh, Arun, Kumar, Singh. (2021). Study the Socio-economic and Communication Profile of the Agricultural Students. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 10(01):1019-1024. https://typeset.io/papers/study-the-socio-economic-and-communication-profile-of-the-48msh1wizr
19. Venkatesh, Viswanath; Thong, James Y. L.; & Xu, Xin (2016). "Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology: A Synthesis and the Road Ahead." Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 17(5). DOI: 10.17705/1jais.00428. Available at: https://aisel.aisnet.org/jais/vol17/iss5/1