CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND
Introduction
Parental involvement in child's education has long been recognized as a critical factor in shaping academic success. Research has shown that parental support, including parental encouragement, communication, and involvement in school activities, plays a vital role in supporting student’s academic achievement.
According to Hill and Tyson (2009), suggest that in Humanities and Social Sciences, where critical thinking and analytical skills are crucial, parental support plays a key role in shaping students engagement and success. Research shows that children whose parents actively engage in their education by monitoring academic progress and fostering a positive learning environment often perform better academically.
In addition, Epstein (1995), reveal that parent involvement happened to families and communities who take an active role in creating a caring educational environment. She further asserted that parents who are involved with their children's education are those who consistently demonstrate good parenting skills, communicate with the school staff, volunteer their time in the school, help their children learn at home, take an active role in school-related decision making, and who regularly collaborate with the school community.
Researchers at Nasugbu East Senior High School want to asses the Influence of Parental Support on Academic Performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students. They also aim to gather data on the Influence of Parental support on Academic Performance among students in order to create educational programs that will offer valuable insights on this topic.
Background of the Study
Research studies have shown that students who receive strong parental support tend to have higher grades, better attendance records, and improved behavior in school. Parents who are actively involved in their child’s education demonstrate a commitment to their academic success and create a supportive home environment that fosters learning and growth.
The study conducted by Bryan (2005) Stated that Children are likely to excel in academics when their parents actively participate in their education. Furthermore, parental support has been found to contribute to the development of important skills such as time management, organization and study habits, of all which are essential for academic success. Zaff (2017) suggested that schools should make efforts to include parents more in the school for example, by training teachers to build relationship and strengthen communication with parents. When parents are engaged in their child’s education, they can provide guidance, resources, and encouragement that help students overcome challenges and reach their full potential.
The researchers utilized the descriptive research design in assessing the Influence of Parental Support on Academic Performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students at Nasugbu East Senior High School. The findings were the bases for the proposed educational program that will offer valuable insights on this topic.
Statement of the Problem
The study aimed to evaluate the Influence of Parental Support on Academic Performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students at Nasugbu East Senior High School. Brgy Lumbangan Nasugbu, Batangas Academic year 2024 -2025. Specifically, the study sought answers to the following questions:
1.How does parental involvement in homework affects students’ academic achievement?
2. What are the effect of parental involvement in school activities on students’ academic achievements?
3.What actionable proposal should be developed to enhance the achievements of the students’ academic performance?
Scope and Limitation of the Study
The study used descriptive research focusing on the Impact of Parental Support on Academic performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students in Nasugbu East Senior High School. Barangay Lumbangan Nasugbu, Batangas.
The study was limited only to Humanities and Social Sciences Students from the aforementioned school. The data were solely gathered from the respondents’ answers in the survey questionnaire. The findings were the bases for the proposed educational program for students that will contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject.
Definition of Terms
These are the conceptual and operational definitions of the following words and phrases used in this study for clearer understanding of the research:
Parental Support. Parental support is the involvement and assistance provided by parents that contributes to their children's emotional and developmental well-being. This support includes offering guidance, resources, and encouragement to help children navigate academic and personal challenges, thereby enhancing their overall growth and achievement (Wang, M., & Sheikh-Khalil, S. 2024). In this study, it refers to the specific actions and behaviors of parents aimed at assisting their children with academic tasks, offering emotional encouragement, and providing resources and guidance.
Parental Encouragement. Parental encouragement is the supportive and motivating behavior exhibited by parents aimed at enhancing their children’s development. This includes providing positive reinforcement, expressing confidence in their abilities, and actively participating in their activities to boost their self-esteem social skill, and overall growth (Lata, 2013). In this study, it’s defined as the process undertaken by the parents to initiate and direct towards higher academic achievement.
Critical Thinking. Critical thinking is self-guided, self-disciplined thinking which attempts to reason at the highest level of quality in a fair-minded way. People who think critically consistently attempt to live rationally, reasonably, empathically (Linda Elder, 2007). In this study, it refers to the student’s capacity to systematically analyze and evaluate arguments and information. This includes the ability to assess the validity of reasoning, identify logical fallacies, and apply sound reasoning to make informed decisions.
Analytical Skills. Analytical skills involve the ability to think critically, differentiate, organize, and attribute information. They are essential for problem-solving and decision-making processes in various academic and professional fields (Septi Budi Sartika, 2018). In this study, it refers to the student’s ability to systematically examine and interpret complex information, including the capacity to identify patterns, draw logical conclusions, and evaluate evidence critically to solve problems or make informed decisions.
Excel. Excel in academic purposes refers to achieving high standards in governance, leadership, strategic planning, performance, quality management, teaching innovation, research, and consulting for academic excellence (Nabeel A. Jurdi, 2019). In this study, it refers to the student’s ability to perform at a high level in their academic tasks, demonstrating superior understanding and application of the material, achieving above-average grades, and showing exceptional skills and competence in their subject area.
Commitment. Commitment involves risks and burdens, and parties are liable for misrepresentation, acquiring proprietary information, and breaking promises (James Gordley, 2023). In this study, it refers to the students’ dedication to consistently engaging with their academic responsibilities, including the willingness to invest time and effort in their studies, adhere to deadlines, and persist through challenges to achieve their educational goals.
Time Management. Time management is the process of organizing, planning and controlling time to get more and better work done in less time. It is defined as “behaviors that aim at achieving an effective use of time while performing certain goal-directed activities (Claessens, 2007). In this study, it refers to the student’s capacity to plan and organize their schedule effectively, including the ability to prioritize tasks, allocate appropriate time for each activity, and meet deadlines.
Study Habits. Study habits are at the core of a learner's academic success. It is an action like reading, taking notes, conducting study groups that students perform frequently, and regularly accomplishing the learning goals (Jhoselle Tus, 2020). In this study, it refers to the student’s consistent practices and strategies for engaging with learning materials, including the frequency and duration of study sessions, the use of specific techniques such as note-taking and self-testing, and the ability to manage and organize study time effectively to enhance comprehension and retention of academic content.
Aforementioned. Aforementioned refers to any item, term, or concept that has been previously mentioned in a text. It functions to direct the reader's attention back to prior references without repeating the details (Taylor, R. 2024). In this study, it refers to information, concepts, or factors that have been previously introduced or discussed, allowing for concise and efficient reference to those earlier points in the text.
Solely. Solely means that a particular factor or element is the only one contributing to or responsible for an outcome. It excludes any other influences or components. For instance, when a researcher claims that a phenomenon is "solely due to" a specific variable, it implies that no other factors are involved or considered (Smith, J. 2022). In this study, its indicates that a particular outcome or result is attributed exclusively to one factor, with no influence from other variables. It is used to emphasize that the specified factor is the only one contributing to the observed effect.
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURES
This chapter presents an intensive review of related literatures found to be relevant to the present study. This chapter likewise includes conceptual and theoretical frameworks, and research simulacrum.
Impact of Parental Involvement on Student Homework Performance
According to Wang and Li (2024), Parental involvement in homework can affect student learning outcomes differently depending on levels of societal collectivism versus individualism.
In addition, this study theorizes three parenting approaches based on parental expectations, evaluations, and networks “Normative parenting”, “Reactive parenting”, and “competitive parenting”, to examine parental involvement and its consequences on academic achievement Li (2024)
The study underscores the importance of parental involvement, including helping with Homework, discussing school -related topics, maintaining a welcoming environment and fostering open communication between parents and teachers Dokmen (2017).
Similarly, Mbathas (2018) study at the University of the free state, States, there is need to develop a framework for parental involvement to improve students’ academic performance, driven by Yosso’s Community Cultural Wealth theory.
Lastly, operationalized parental involvement as a multidimensional construct in terms of quantity and quality and examined how the quantity and different qualities of homework involvement were associated with student achievement Moroni et al. (2015).
Effects of parental involvement in school activities on students academic achievements
According to, Wilders (2023) meta-synthesis examined nine meta -analysis and found that parental involvement positively influences academic performance, regardless of how it is defined. Notably, parental expectations for success had the strongest effect, while assistance with homework was the weakest.
In addition, Gokturk and Dinckal (2018) findings of this collective case study demonstrate there are important misunderstandings and related tensions among parents and teachers over the roles of each party. Teachers believe that parents’ educational roles are mostly performed at home. On the contrary, parents are shown as having a higher desire to participate in educational decisions.
The data was analyzed by using frequency analysis to find out the frequencies and the percentages of the demographic characteristics of the participants and the frequencies of the parents’ responses on the questions regarding their involvement in student academic achievement Chaudry (2015).
Similarly, Results indicate that active parental involvement positively improves academic outcomes, including behavior, attendance, and grades. Conversely, learners with less engaged parents tend to show limited progress in their academic performance Agbayani (2024).
Lastly, there is a strong belief in society that parental involvement has a strong positive effect on students’ academic performance. Student learning not only takes place in schools but also the contexts of families and communities play a great role (Ma, Shen, Krenn, Hu & Yuan, 2016).
Theoretical Framework This study was grounded in Bronfenbrenner's Ecological Systems Theory (1979) as cited by Botha, Kourkoutas which emphasizes the interplay between individual development and the various environmental contexts surrounding a child. According to this theory, the family unit serves as the immediate environment that significantly shapes a child's academic experiences. Parental support-encompassing emotional encouragement, active involvement in school activities, and academic assistance-can enhance a child's motivation, self-esteem, and overall academic performance.
Additionally, this theory further elucidates the mechanisms through which parental support impacts academic achievement. This theory posits that children learn behaviors and values by observing and interacting with their parents. When parents engage in educational activities and demonstrate positive attitudes toward learning, children are likely to adopt similar behaviors and beliefs. This modeling can lead to improved academic performance as children internalize the importance of education through their parents' actions.
Moreover, To study a child's development then, we must look not only at the child and her immediate environment, but also at the interaction of the larger environment as well.
Conceptual Framework
Based on the explained conceptual theory used in this study, the researcher identified that in order to develop in-depth knowledge and careful judgment about the relationships between the variables, it required a critical analysis of how parental support influences the academic performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) students.
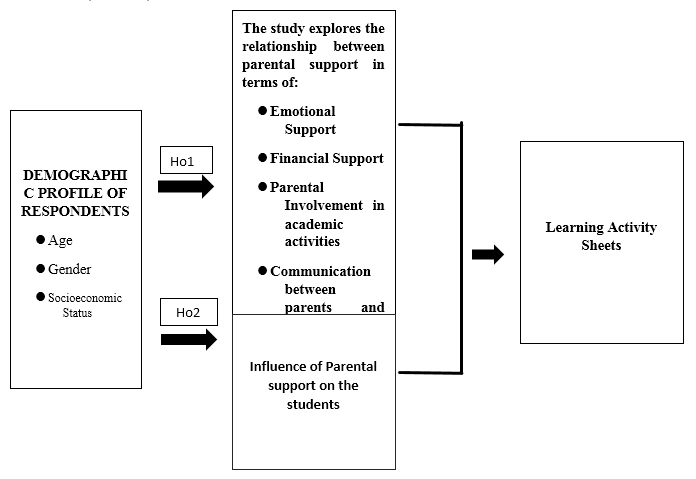
Figure (1) illustrates the research model of the study. It shows the relationship between the different types of parental support (emotional, financial, involvement in academics, and communication) and academic performance (grades, class participation, and academic engagement), as well as the role of the demographic profile (age, gender, socioeconomic status) in moderating these relationships. The figure also highlights the challenges in enhancing parental involvement and how Learning Activity Sheets can be designed to address these challenges and improve academic outcomes.
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODS AND PROCEDURES
This chapter presents the methods of research used. It also includes the research design, locale and respondents of the study, research instrument, construction and validation of instrument, ethical considerations, data gathering procedures and statistical treatment of data.
Research Design
The study employed a descriptive research design to assess the influence of parental support on the academic performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences students. According to Scibbr (2019), descriptive research design aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation, or phenomenon. It allows the researcher to use a variety of methods to investigate one or more variables relevant to the study. In this research, the descriptive method was utilized by gathering data regarding the level of parental support and the academic performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences students. The study focused on key variables including emotional support, financial support, parental involvement in academic activities, and communication between parents and students. These variables were chosen for their significance in understanding how parental support can impact the academic achievements of students.
Locale of the Study
The study was conducted in Nasugbu East Senior High School located at Brgy. Lumbangan, Nasugbu, Batangas. It was founded in the year 2016. The school was headed by Principal ll, with forty-six (46) teachers and nine (90) non-teaching staff it has a total population of one thousand three hundred three (1,303) enrolled students comprises the grade 11 and 12. There are total of two hundred seventy-nine (279) population of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students this School Year 2023-2024. The school offers academic which includes Accountancy, Business and Management (ABM) strand, Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) strand, Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) strand, Technical, Vocational, and Livelihood Track (TVL).
Respondents of the Study
The researcher utilized Slovin's formula to compute the necessary sample size for the study population. Slovin's formula helps determine the sample size required to achieve a certain confidence interval when sampling a population. For this study, a sample size of one hundred seventy-nine (179) respondents was recommended, with a 95% confidence level and a 5% margin of error. This calculation was deemed suitable for representing the target population. The respondents were selected using Simple Random Sampling (SRS), which ensures that every individual in the population has an equal chance of being chosen. This method provides a fair and unbiased selection process, often referred to as the "Method of Chance Selection," where every participant has an equally likely opportunity to be included in the sample.
Research Instrument
The researcher reviewed various literature in speculative assertion to construct the instrument of the study. A survey questionnaire was developed from these literatures and was utilized to gather pertinent data for the present.
Part I was to examine the relationship between parental support and academic performance. Additionally, analyze the data by demographic factors such as gender and major subject area.
Part II was a self-reported measure and may be subject to biases and inaccuracies. Future studies may consider using multiple informants or objective measures of academic performance it was rated on a 4-point scale as follows 1 =Strongly Disagree, 2 = Disagree, 3 =Agree, 4 = Strongly Agree.
Construction, and Validation of the Instrument
The research instrument designed to assess the influence of parental support on the academic performance of Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences students was carefully developed with the guidance of our thesis adviser. We worked closely with our adviser, gathering feedback and refining the questions to ensure they aligned with the research goals. After making necessary revisions, the questionnaire was then reviewed by other experts in education, who provided additional insights to make sure each question accurately captured the different aspects of parental support and its impact on academic performance. The careful review helped ensure that the instrument had strong content validity. Moreover, these steps were crucial in ensuring both the reliability and validity of the tool, allowing us to gather data that would lead to meaningful and accurate results.
Ethical Considerations
In this study, ethical considerations were prioritized to ensure the protection and rights of the respondents. The consent of each respondent was obtained before their participation. Each Grade 12 HUMSS student involved in the research was provided with a consent form, which was thoroughly explained to ensure that they fully understood the purpose and nature of the study. It was emphasized that their participation was entirely voluntary, and they were informed of their right to withdraw from the study at any time without consequence. The researcher adhered to ethical principles, including respect for autonomy, confidentiality, and non-maleficence, to maintain the dignity and integrity of all respondents throughout the research process.
Data Gathering Procedure
Prior to data collection, permission was sought and granted by the school principal of [School Name] and the public-school district supervisor to conduct research on assessing the influence of parental support on the academic performance of Grade 12 HUMSS students. The request letter (Appendix A) was submitted to the Office of the School Principal for review. Upon approval, the researcher scheduled a meeting with the respondents to explain the purpose of the study, ensuring that participants understood the research objectives and procedures. Respondents were also encouraged to ask questions to address any concerns about their participation. Following the orientation, survey questionnaires were distributed to the target respondents. The questionnaire was designed to gather data on parental support and its correlation with the academic performance of the students. Ample time was provided for the respondents to thoughtfully and honestly answer the questions. In addition, the researcher carefully monitored the completion of the questionnaires and ensured that all were fully answered before retrieval.
Statistical Treatment of Data
The following statistical tools were employed to analyze the data gathered in this study:
Problem 1: Demographic Profile of the Respondents Frequency and Percentage. These were used to describe and summarize the demographic characteristics of the respondents, such as age, sex, and socio-economic status. The frequency and percentage distributions were calculated to show the proportion of respondents under each demographic category.
Problem 2: Level of Parental Support Weighted Mean and Standard Deviation. These statistical measures were used to analyze the level of parental support perceived by the Grade 12 HUMSS students. The weighted mean was utilized to determine the average level of support, while the standard deviation was used to measure the variability in the responses.
Problem 3: Academic Performance of Grade 12 HUMSS Students Weighted Mean and Standard Deviation. These were also used to assess the academic performance of the respondents. The weighted mean helped in identifying the general trend in students' performance, while the standard deviation measured the consistency of their academic performance scores.
CHAPTER 4
PRESENTATION ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION DATA
This part presents the data gathered, analysis and interpretation To answer the problem which this study aims to achieve.
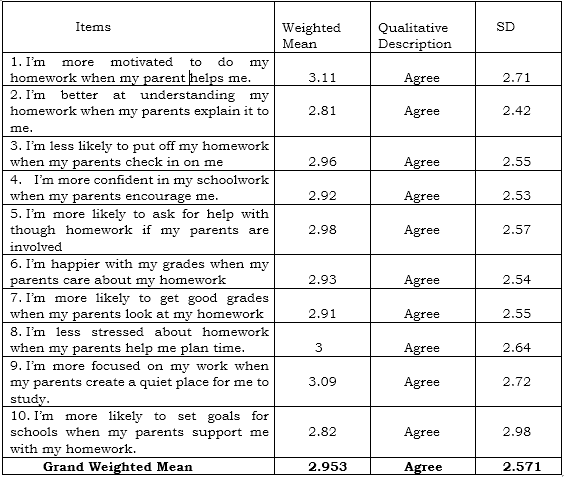
1. Impact of Parental Involvement in Homework
Table 1 presents the impact of parental involvement in homework. Based on the ten (10), indicators which are presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey. The weighest weighted mean is the respondents’ answers regarding that students are motivated to do their homework when their parents help them with weighted mean of 3.11 (SD = 2.71) Qualitatively describes as Agree. It shows that students are more motivated when their parent help them. However, students became better in understanding their homework when their parents explain it to them, and it has lowest weighted mean of 2.81 (SD = 2.42) which means student appreciate the topic. This indicator is Qualitatively described as Agree.
Overall result shows that respondents mark “Agree” on the Parental Involvement in Homework with Grand Weighted mean of 2.953 (SD = 2.571).
This result is related to the study conducted by Bryan (2005) stated that children are likely to excel in academic when their parents actively participate in their education. This explain that Parental Support is crucial for students to develop academic excellence.
Table 1 Impact of Parental Involvement in Homework
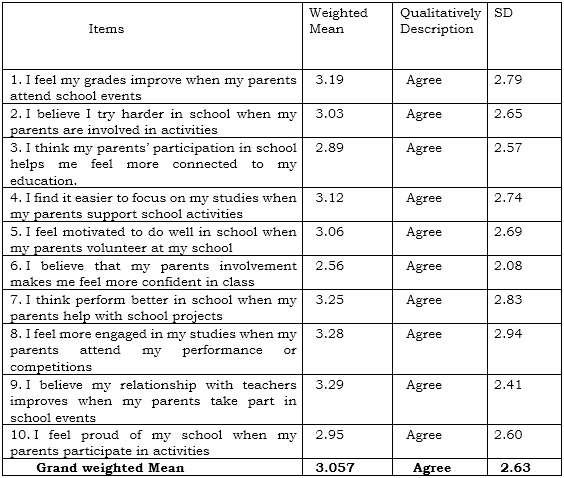
2. Impact of Parental Involvement in School Activities on Students Academic Achievement
Table 2 Presents the Impact of Parental Involvement in School activities on Students Academic Achievement. Based on the ten (10) indictors which are the presented to the respondents during the conduct of the survey, the highest weighted mean is the respondents answers regarding about the relationship with teachers improves when parents take part in school events with weighted mean of 3.29 (SD = 2.41), qualitatively describes as agree. This means that parental support in school events really improves relationship with teachers, However, parents’ involvement makes student feels more confident in class with the lowest weighted mean of 2.56 (SD = 2.08) which means students appreciate the topics. This indicator is qualitatively described as agree.
Overall, results show that the respondents mark “Agree” on impact of parental involvement in school activities on students with grand weighted mean of 3.057 (SD = 2.63).
This result is related to the study conducted by Epstein (1995) shows that parent involvement happened to families and communities who take on active role in creating educational environment. This explained that parent involvement in education create a caring educational environment.
Table 2 The effects of Parental Involvement in School Activities on the Academic Achievement
CHAPTER 5
Summary, Conclusion, and Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of findings, conclusion, and recommendations of the study.
Summary of Findings
1. The impact of parental involvement in homework affects students’ academic achievement.
The findings showed the respondents agreed on parental involvement in homework with grand waited mean 10.52(SD=2.72)
2. Effects of parental involvement in school's activities on student academic achievement.
The findings showed the respondents agreed that parental involvement has big effects on student academic performance with grand waited mean 11.96(SD=2.94)
3. Actionable proposal to enhance the achievement of students’ academic performance.
The researcher's proposed actionable proposal to enhance the achievement of students’ academic performance.
Conclusion
Based on findings of the study, the following conclusions are drawn:
1. The findings show clear consensus among the respondents, indicating that active parental engagement in homework and participation on school activities.
2. The study proposes actionable strategies to further enhance students' academic outcomes. Schools can foster an environment where both students and parents contribute to the overall educational experience, ultimately leading to improved student performance.
Recommendation
Based on the proceeding findings and conclusions the following recommendations are offered by the researchers.
1. Encourage open and supportive communication between parents and students. Schools can provide resources or counseling services to help families foster constructive conversations about academic expectations, goals, and challenges, ensuring that students feel emotionally supported in their educational journey.
2. Schools should establish or strengthen programs that encourage active parental involvement in students' academic lives. Workshops, seminars, and regular communication between teachers and parents can increase awareness of the academic challenges students face and provide parents with the tools to offer targeted support at home.
3. Schools should adopt strategies to create a partnership between educators and families. This might include regular progress updates, parent-teacher conferences, and creating platforms for parents to discuss their children's academic needs.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Abdul Qayyum Chaudhry(2015) Parent's involvement in their child academic achievement https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=rrl%20about%20the%20effects%20of%20parental%20involvement%20in%20school%20activities%20on%20students%20academic%20achievement%20&btnG=&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR0mfzryfo3jx-Q4O_4MPzGGdKx7T69jgLWxXV98_hRdmVkg9t7YaWIZTIk_aem_xRmS5W5clGQbjSD34Ocx2Q - d=gs_qabs&t=1726179570724&u=%23p%3D9quoHHDpMq4J
Bryan (2005), “The Impact of Parental Involvement on Aademic Achievement “ http://gateway.proquest.com/openurI?url_ver=Z39.88-2004&rtf_val_fmt=info:ofi/fmt:kev:mtx:dissertion&res_dat=xri:pqm&rtf_dat=xri:pqdiss:10602196
Claessens, (2007). *Time management" https://www.kbmanage.com/concept/time-management#
Dokmen (2017) The impact of Parental Involvement on the Academic Achievement of Students in Urban Charter Schools https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=RRL%202015%20about%20how%20does%20parental%20involvement%20in%20homework%20affect%20student%20academic%20achievement&btnG=&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR0aWKH0yvT7NknxfW6u3poekeQt-qDXcTWyVs5g_EYJMo9mS754oKb_wZ8_aem_4TkJat12BVfzgl7H15jykQ - d=gs_qabs&t=1726392872536&u=%23p%3DUAMoYPGS04IJ
JRF Galang, JL Dungca, GY Agbayani (2024) Parental Involvement in Curricular Performance of Students at Risk https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=Rrl%20for%20the%20effects%20of%20parental%20involvement%20in%20school%20activities%20on%20students%20academic%20achievement%20&btnG.x=65&btnG.y=12&hl=en&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR1MrOHcDaOJRtgsbXD8wfM5fAI2ZfXJx_sjSgtw2yqjzyrZkNNqyKRODww_aem_yTg2rkz4mDyYOu_lzkBAjQ - d=gs_qabs&t=1726177806544&u=%23p%3DChh-gFKngp0J
James Gordley, (2023) COMMITMENT https://typeset.io/papers/commitment-2zbye41qbx Lata, (2013). "A Study of Parental Encouragement, Educational Adjustment and Academic Achievement among Adolescent Students of District Anantnag" https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://ijip.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/18.01.093.20231101.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwjzprHAxLiIAxWGh1YBHXz7F5cQFnoECBoQBg&usg=AOvVaw0cBgQDh4h4DK2gGfC8hsCo
Jhoselle Tus, (2020). *The learners' study habits and its relation on their academic performance" https://typeset.io/search?q=The%20learners%27%20study%20habits%20and%20its%20relation%20on%20their%20academic%20performance Linda Elder, (2007) "The foundation for Critical Thinking" https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766
Li (2024) Parenting Approaches, Parental Involvement, and Academic Achievement in US Elementary Schools https://eric.ed.gov/?q=rrl%20of%20how%20does%20parental%20involvement%20in%20homework%20affect%20students%20academic%20achievement%20&id=EJ1432248&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR3IPeByIrT7U9rhQrnK9soYj20Gea8kJouRH52NpCWow5uRt_8ib-RwZdU_aem_uIAKpPRWoeB2Qw9uSr8Tpw
Ma, Shen, Krenn, Hu & Yuan (2016) A Meta-analysis of the Effect of Parental Involvement on Students Academic Achiement https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https%3A%2F%2Ffiles.eric.ed.gov%2Ffulltext%2FEJ1280652.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwie9PW4rsSIAxVg7TgGHc9WIAUQFnoECBUQAQ&usg=AOvVaw2mAHtqb2A9dC94zyv161Ch&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR0mfzryfo3jx-Q4O_4MPzGGdKx7T69jgLWxXV98_hRdmVkg9t7YaWIZTIk_aem_xRmS5W5clGQbjSD34Ocx2Q
Nabeel A. Jurdi, (2019). *The Concept of Academic Excellence: A Macro Analysis" https://typeset.io/papers/the-concept-of-academic-excellence-a-macro-analysis-1xeg3vfd4c
Septi Budi Sartika, (2018). Teaching Models to Increase Students' Analytical Thinking Skills https://typeset.io/papers/teaching-models-to-increase-students-analytical-thinking-152b0ere5r
Mbathas (2018) Developing a framework of Parental Involvement to Enhance academic performance of learners in schools https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Developing%20a%20Framework%20for%20Parental%20Involvement%20to%20Boost%20Academic%20Performance%20Zwelinjane%20Meshack%20Mbatha%2C%20University%20of%20the%20Free%20State%2C%202018&btnG=&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR0aWKH0yvT7NknxfW6u3poekeQt-qDXcTWyVs5g_EYJMo9mS754oKb_wZ8_aem_4TkJat12BVfzgl7H15jykQ - d=gs_qabs&t=1726393149398&u=%23p%3DJF40J78dJpMJ
Smith, J. (2022). The Art of Precision: Defining Key Terms in Research. https://www.academicinsights.com/precision-key-terms](https://www.academicinsights.com/precision-key-terms) .
Taylor, R. (2024). Clarity in Academic Writing: The Role of Reference Terms. Academic Journal. [ https://www.academicjournal.com/clarity-in-writing](https://www.academicjournal.com/clarity-in-writing)
Moroni et al. (2015) Antecedents and outcomes of Parental Homework Involvement: How do Family-school Partenrships Affect Parental Homework Involvement and Student outcomes https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01048/full Wilders (2023), Effects of parental involvement on academic achievements: A meta – synthesis https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781003403722-12/effects-parental-involvement-academic-achievement-meta-synthesis-wilder?fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR1MrOHcDaOJRtgsbXD8wfM5fAI2ZfXJx_sjSgtw2yqjzyrZkNNqyKRODww_aem_yTg2rkz4mDyYOu_lzkBAjQ Wang, M., & Sheikh-Khalil, S. (2024). Measuring Parental Support: Conceptual and Operational Perspectives. Child Development Research, 62(3), 115-134. [ https://www.childdevelopmentresearch.com/measuring-parental-support](https://www.childdevelopmentresearch.com/measuring-parental-support) Wang & LI (2024) Relationships between Parental Involvement In Homework and Learning Outcomes among Elementary School Student: The Moderating Rule of Societal Collectivism –Indivual lid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR0mfzryfo3jx-Q4O_4MPzGGdKx7T69jgLWxXV98_hRdmVkg9t7YaWIZTIk_aem_xRmS5W5clGQbjSD34Ocx2Q Soheyda Gokturk, Selin Dinckal (2018) Effective parental involvement in education: experiences and perceptions of Turkish teachers from private schools https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=rrl%20about%20the%20effects%20of%20parental%20involvement%20in%20school%20activities%20on%20students%20academic%20achievement%20&btnG=&fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR1jzqL731w5xBm6xHnqLkXDwYGpSlAnT96powJVaI0jSJsQmVtj5cwrzDg_aem_YQZ2shy_e9f7gsseQoVmqg - d=gs_qabs&t=1726180004617&u=%23p%3DZ9mUUrxA9BMJ
Zaff (2017)”Parental Involvement and Educational Success Among vulnerable students in vocational education and training” https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00131881.2021.1988672#abstracthttp://gateway.proquest.com/openurI?url_ver=Z39.88-2004&rtf_val_fmt=info:ofi/fmt:kev:mtx:dissertion&res_dat=xri:pqm&rtf_dat=xri:pqdiss:10602196